Simultaneous detection of multiple fish pathogens using a naked-eye readable DNA microarray
- PMID: 22736973
- PMCID: PMC3376613
- DOI: 10.3390/s120302710
Simultaneous detection of multiple fish pathogens using a naked-eye readable DNA microarray
Abstract
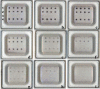
We coupled 16S rDNA PCR and DNA hybridization technology to construct a microarray for simultaneous detection and discrimination of eight fish pathogens (Aeromonas hydrophila, Edwardsiella tarda, Flavobacterium columnare, Lactococcus garvieae, Photobacterium damselae, Pseudomonas anguilliseptica, Streptococcus iniae and Vibrio anguillarum) commonly encountered in aquaculture. The array comprised short oligonucleotide probes (30 mer) complementary to the polymorphic regions of 16S rRNA genes for the target pathogens. Targets annealed to the microarray probes were reacted with streptavidin-conjugated alkaline phosphatase and nitro blue tetrazolium/5-bromo-4-chloro-3'-indolylphosphate, p-toluidine salt (NBT/BCIP), resulting in blue spots that are easily visualized by the naked eye. Testing was performed against a total of 168 bacterial strains, i.e., 26 representative collection strains, 81 isolates of target fish pathogens, and 61 ecologically or phylogenetically related strains. The results showed that each probe consistently identified its corresponding target strain with 100% specificity. The detection limit of the microarray was estimated to be in the range of 1 pg for genomic DNA and 10(3) CFU/mL for pure pathogen cultures. These high specificity and sensitivity results demonstrate the feasibility of using DNA microarrays in the diagnostic detection of fish pathogens.
Keywords: 16S rDNA; fish pathogen detection; naked-eye reading microarray.
Figures


References
-
- Lu C.P. Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila and the fish diseases caused by it. J. Fish. China. 1992;16:282–288.
-
- Egusa S. Some bacterial diseases of freshwater fishes in Japan. Fish Pathol. 1976;10:103–114.
-
- Liu C.I., Tsai S.S. Edwardsielosis in pond-cultured eel in Taiwan. CAPD Fish. Ser. 3 Rep. Fish Dis. Res. 1980;3:108–115.
-
- Nakatsugawa T. Edwardsiella tarda isolated from cultured young flouders. Fish Pathol. 1983;18:99–101.
-
- Aoki T., Kitao T. Drug resistance and transferable R plasmids in Edwardsiella tarda from fish culture ponds. Fish Pathol. 1981;15:277–281.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

