Robust facial expression recognition via compressive sensing
- PMID: 22737035
- PMCID: PMC3376615
- DOI: 10.3390/s120303747
Robust facial expression recognition via compressive sensing
Abstract
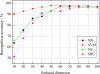
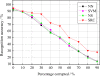
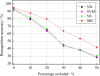
Recently, compressive sensing (CS) has attracted increasing attention in the areas of signal processing, computer vision and pattern recognition. In this paper, a new method based on the CS theory is presented for robust facial expression recognition. The CS theory is used to construct a sparse representation classifier (SRC). The effectiveness and robustness of the SRC method is investigated on clean and occluded facial expression images. Three typical facial features, i.e., the raw pixels, Gabor wavelets representation and local binary patterns (LBP), are extracted to evaluate the performance of the SRC method. Compared with the nearest neighbor (NN), linear support vector machines (SVM) and the nearest subspace (NS), experimental results on the popular Cohn-Kanade facial expression database demonstrate that the SRC method obtains better performance and stronger robustness to corruption and occlusion on robust facial expression recognition tasks.
Keywords: Gabor wavelets representation; compressive sensing; corruption and occlusion; facial expression recognition; local binary patterns; sparse representation.
Figures




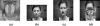
References
-
- Picard R.W. Affective Computing. The MIT Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2000.
-
- Tian Y., Kanade T., Cohn J. Handbook of Face Recognition. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2005. Facial expression analysis; pp. 247–275.
-
- Viola P., Jones M. Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vision. 2004;57:137–154.
-
- Heisele B., Serre T., Poggio T. A component-based framework for face detection and identification. Int. J. Comput. Vision. 2007;74:167–181.
-
- El-Bakry H.M. New fast principal component analysis for real-time face detection. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2009;18:405–425.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

