Genetic ancestry-smoking interactions and lung function in African Americans: a cohort study
- PMID: 22737244
- PMCID: PMC3380861
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039541
Genetic ancestry-smoking interactions and lung function in African Americans: a cohort study
Abstract
Background: Smoking tobacco reduces lung function. African Americans have both lower lung function and decreased metabolism of tobacco smoke compared to European Americans. African ancestry is also associated with lower pulmonary function in African Americans. We aimed to determine whether African ancestry modifies the association between smoking and lung function and its rate of decline in African Americans.
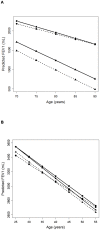
Methodology/principal findings: We evaluated a prospective ongoing cohort of 1,281 African Americans participating in the Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study initiated in 1997. We also examined an ongoing prospective cohort initiated in 1985 of 1,223 African Americans in the Coronary Artery Disease in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Pulmonary function and tobacco smoking exposure were measured at baseline and repeatedly over the follow-up period. Individual genetic ancestry proportions were estimated using ancestry informative markers selected to distinguish European and West African ancestry. African Americans with a high proportion of African ancestry had lower baseline forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV₁) per pack-year of smoking (-5.7 ml FEV₁/ smoking pack-year) compared with smokers with lower African ancestry (-4.6 ml in FEV₁/ smoking pack-year) (interaction P value = 0.17). Longitudinal analyses revealed a suggestive interaction between smoking, and African ancestry on the rate of FEV(1) decline in Health ABC and independently replicated in CARDIA.
Conclusions/significance: African American individuals with a high proportion of African ancestry are at greater risk for losing lung function while smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Smoking-attributable mortality, years of potential life lost, and productivity losses–United States, 2000–2004. MMWR. 2008;57:1226–1228. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tobacco use among U.S. racial/ethnic minority groups–African Americans, American Indians and Alaska Natives, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders, Hispanics. A Report of the Surgeon General. Executive summary. MMWR Recomm Rep 47: v-xv, 1–16. 1998. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Stable EJ, Herrera B, Jacob P, 3rd, Benowitz NL. Nicotine metabolism and intake in black and white smokers. JAMA. 1998;280:152–156. - PubMed
-
- Hankinson JL, Odencrantz JR, Fedan KB. Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general U.S. population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:179–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI061774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095095/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AG-6-2103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079139/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL078885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95095/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23HL093023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48050/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL078885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI077439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048047/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AG-6-2106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064695/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI079139/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL088133/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI077439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AG-6-2101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL092601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48047/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL093023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI061774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL74104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48049/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK064695/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48048/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL079055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL092601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088133/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

