Optical coherence tomographic findings in highly myopic eyes
- PMID: 22737340
- PMCID: PMC3380683
Optical coherence tomographic findings in highly myopic eyes
Abstract
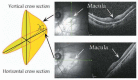
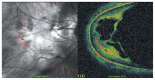
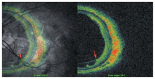
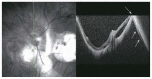
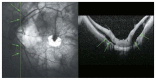
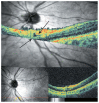
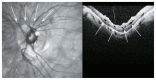
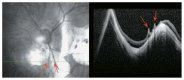
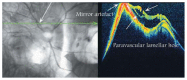
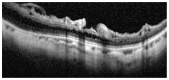
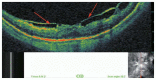
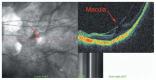
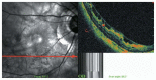
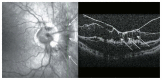
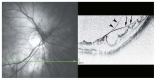
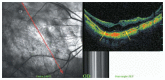
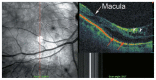
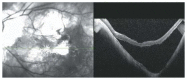
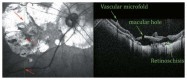
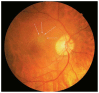
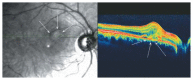
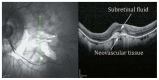
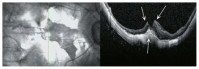
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has enhanced our understanding of changes in different ocular layers when axial myopia progresses and the globe is stretched. These findings consist of dehiscence of retinal layers known as retinoschisis, paravascular inner retinal cleavage, cysts and lamellar holes, peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation, tractional internal limiting membrane detachment, macular holes (lamellar and full thickness), posterior retinal detachment, and choroidal neovascular membranes. In this review, recent observations regarding retinal changes in highly myopic eyes explored by OCT are described to highlight structural findings that cannot be diagnosed by simple ophthalmoscopy.
Keywords: High Myopia; OCT; Optical Coherence Tomography.
Figures
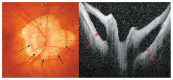
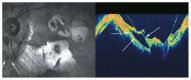
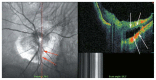
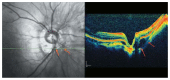


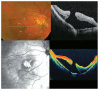
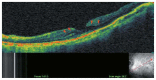
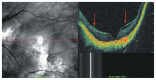
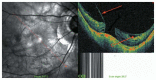
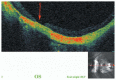
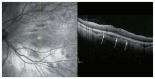
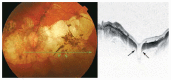
References
-
- Curtin BJ. Physiologic vs pathologic myopia: genetics vs environment. Ophthalmology. 1979;86:681–691. - PubMed
-
- Balacco-Gabrieli C. Aetiopathogenesis of degenerative myopia: a hypothesis. Ophthalmologica. 1982;185:199–204. - PubMed
-
- Forte R, Pascotto F, Soreca E, Cusati G, de Crecchio G. Posterior retinal detachment without macular hole in high myopia: visualization with en face optical coherence tomography. Eye. 2007;21:111–113. - PubMed
-
- Forte R, Cennamo G, Pascotto F, de Crecchio G. En face optical coherence tomography of the posterior pole in high myopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;145:281–288. - PubMed
-
- Wang K, Ding Z, Zeng Y, Meng J, Chen M. Sinusoidal B-M method based spectral domain optical coherence tomography for the elimination of complex-conjugate artifacts. Opt Express. 2009;17:16820–16833. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
