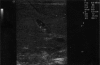
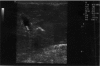
Prevalence of asymptomatic gallstone in healthy neonates in shiraz, southern iran
- PMID: 22737426
- PMCID: PMC3371891
Prevalence of asymptomatic gallstone in healthy neonates in shiraz, southern iran
Keywords: Asymptomatic; Gallstone; Iran; Neonate; Prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brown DL, Teele RL, Doubilet PM, Disalvo DN, Benson CB, Van Alstyne GA. Echogenic material in fetal gallbladder: Sonographic and clinical observations. Radiology. 1992;182:73–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources