Thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy in rat: behavioral, biochemical and histological changes
- PMID: 22737573
- PMCID: PMC3372030
Thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy in rat: behavioral, biochemical and histological changes
Abstract
Background: As a serious neuropsychiatric disease, hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a clinical condition with several types regarding chronicity and clinical diversity that can develop as a complication of both acute and chronic liver failure. This study evaluates changes in thioacetamide (TAA)-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy (AHE) in rat as an animal model.
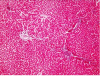
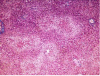
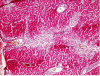
Methods: Both genders of C57BL6, BALB/C mice and Sprague Dawley rats; (10 animals in each group) were compared for induction of AHE to clarify which animal and gender were appropriate. The animals (10 male rats in each group) were categorized in 4 groups according to the dose of the TAA administered (200, 300 and 400 mg/kg of TAA at 24 h intervals for 4 days). A control group was treated with solvent of TAA which was water (5 ml/kg/day). The behavioral, biochemical markers of hepatic failure and histological aspects of thioacetamide (TAA) induced AHE and the correlation between the clinical severity and liver failure biomarkers were evaluated.
Results: Rat was shown to be an animal model of choice for AHE while the optimum dosage of TAA to induce AHE was 300 mg/kg/day at 24 h intervals for 4 days. The behavioral score was partially correlated with the rising of some biomarkers and pathological findings.
Conclusion: Rat can be introduced as the animal of choice for AHE to study the pathophysiology, pharmacology and the survival rate of disease in liver transplant patients.
Keywords: Acute hepatic encephalopathy; Rat; Thioacetamide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Butterworth RF. Pathophysiology of Hepatic Encephalopathy: Studies in Animal Models. In: McCandless DW, editor. Metabolic Encephalopathy. New York: Springer; 2009. pp. 149–180.
-
- Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, Butterworth RF, Morgan MY. International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN). Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy--an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33:739–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04590.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Gibson DP, Heuman DM, Thacker LR, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Luketic V, Fuchs M, White MB, Bell DE, Gilles H, Morton K, Noble N, Puri P, Sanyal AJ. The multi-dimensional burden of cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy on patients and caregivers. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:1646–53. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.157. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
