The proline regulatory axis and cancer
- PMID: 22737668
- PMCID: PMC3380417
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00060
The proline regulatory axis and cancer
Abstract
Studies in metabolism and cancer have characterized changes in core pathways involving glucose and glutamine, emphasizing the provision of substrates for building cell mass. But recent findings suggest that pathways previously considered peripheral may play a critical role providing mechanisms for cell regulation. Several of these mechanisms involve the metabolism of non-essential amino acids, for example, the channeling of glycolytic intermediates into the serine pathway for one-carbon transfers. Historically, we proposed that the proline biosynthetic pathway participated in a metabolic interlock with glucose metabolism. The discovery that proline degradation is activated by p53 directed our attention to the initiation of apoptosis by proline oxidase/dehydrogenase. Now, however, we find that the biosynthetic mechanisms and the metabolic interlock may depend on the pathway from glutamine to proline, and it is markedly activated by the oncogene MYC. These findings add a new dimension to the proline regulatory axis in cancer and present attractive potential targets for cancer treatment.
Keywords: MYC oncogene; glutamine metabolism; proline metabolism; redox regulation; tumor suppressor function.
Figures


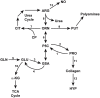

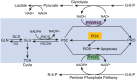
References
-
- Adams E. (1970). Metabolism of proline and of hydroxyproline. Int. Rev. Connect. Tissue Res. 5, 1–91 - PubMed
-
- Anthony B., Allen J., Li Y. S., Mcmanus D. P. (2010). Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced downregulation of hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrogenesis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 25, A9–A9 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

