A pilot study of hippocampal volume and N-acetylaspartate (NAA) as response biomarkers in riluzole-treated patients with GAD
- PMID: 22739126
- PMCID: PMC3473175
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.05.009
A pilot study of hippocampal volume and N-acetylaspartate (NAA) as response biomarkers in riluzole-treated patients with GAD
Abstract
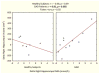
Anxiolytic benefit following chronic treatment with the glutamate modulating agent riluzole in patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) was previously associated with differential changes in hippocampal NAA concentrations. Here, we investigated the association between hippocampal volume and hippocampal NAA in the context of riluzole response in GAD. Eighteen medication-free adult patients with GAD received 8-week of open-label riluzole. Ten healthy subjects served as a comparison group. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy at baseline and at the end of Week 8. GAD patients who completed all interventions were classified as remitters (n=7) or non-remitters (n=6), based on final Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) scores ≤7. At baseline, GAD patients had a significant reduction in total hippocampal volume compared to healthy subjects (F(1,21)=6.55, p=0.02). This reduction was most pronounced in the remitters, compared to non-remitters and healthy subjects. Delta (final-baseline) hippocampal volume was positively correlated with delta NAA in GAD. This positive association was highly significant in the right hippocampus in GAD [r=0.81, p=0.002], with no significant association in healthy subjects [Fisher r-to-z p=0.017]. Across all GAD patients, delta hippocampal volume was positively associated with improvement in HAM-A (rspearman=0.62, p=0.03). These preliminary findings support hippocampal NAA and volume as neural biomarkers substantially associated with therapeutic response to a glutamatergic drug.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. and ECNP. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
JDC receives grant support from NIMH, NYSTEM, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Alexza Pharmaceuticals. He is on the Pfizer advisory board and gives talks for BMS, AstraZeneca, GSK, and Pfizer. SJM: Grant or Research Support: NIMH, NARSAD, Dept. of Veterans Affairs. Consultant (last 24 months): Cephalon, Roche, Noven, AstraZeneca. No biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest are reported for CGA, AJ, JRS, XM, and DCS.
Figures




References
-
- Brennan BP, Hudson JI, Jensen JE, McCarthy J, Roberts JL, Prescot AP, Cohen BM, Pope HG, Jr, Renshaw PF, Ongur D. Rapid enhancement of glutamatergic neurotransmission in bipolar depression following treatment with riluzole. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:834–846. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cavus I, Pan JW, Hetherington HP, Abi-Saab W, Zaveri HP, Vives KP, Krystal JH, Spencer SS, Spencer DD. Decreased hippocampal volume on MRI is associated with increased extracellular glutamate in epilepsy patients. Epilepsia. 2008;49:1358–1366. - PubMed
-
- Duyn JH, Gillen J, Sobering G, van Zijl PC, Moonen CT. Multisection proton MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain. Radiology. 1993;188:277–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

