Hyperglycemia and renal mass ablation synergistically augment albuminuria in the diabetic subtotally nephrectomized rat: implications for modeling diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 22739500
- PMCID: PMC3383305
- DOI: 10.1159/000338272
Hyperglycemia and renal mass ablation synergistically augment albuminuria in the diabetic subtotally nephrectomized rat: implications for modeling diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMSBACKGROUND/AIMS: While experimental models that emulate diabetic nephropathy are valuable tools for elucidating pathogenetic mechanisms and developing novel therapies, existing models imperfectly recapitulate human disease. In diabetes, hyperglycemia and hemodynamic forces act in concert to induce renal injury. Accordingly, in the present study, we combined streptozotocin-induced diabetes with surgical ablation of 5/6 of the kidney mass with the aim of evaluating their additive effects on renal function and glomerular morphology.
Methods: Female F344 rats were randomized to undergo subtotal nephrectomy (SNx) either at baseline or following 4 weeks of diabetes.
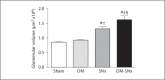
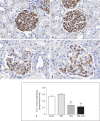
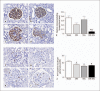
Results: In comparison to sham rats, rats with diabetes or rats after SNx surgery, diabetic subtotally nephrectomized (DM-SNx) rats demonstrated an increase in systolic blood pressure, glomerular volume and mesangial matrix. Albuminuria was synergistically increased by hyperglycemia and renal mass ablation associated with decreased nephrin expression. In contrast, glomerular capillary rarefaction and glomerular filtration rate were similarly reduced in SNx and DM-SNx rats.
Conclusion: The DM-SNx rat recapitulates some of the features of human disease, most notably augmented albuminuria. Since this model avoids the deletion or overexpression of gene(s) linked to the pathogenesis of nephropathy, the DM-SNx rat model represents a complementary tool for the trial of novel therapies.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Diabetic nephropathy; Experimental model; Glomerular hypertrophy; Glomerulosclerosis; Nephrin; Streptozotocin; Subtotal nephrectomy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of ramipril, nifedipine, and moxonidine on glomerular morphology and podocyte structure in experimental renal failure.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996 Jun;11(6):1003-11. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996. PMID: 8671960
-
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 decreases podocyte loss and podocyte hypertrophy in the subtotally nephrectomized rat.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004 Mar;286(3):F526-33. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00316.2003. Epub 2003 Nov 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14600034
-
Reversal of glomerulosclerosis after high-dose enalapril treatment in subtotally nephrectomized rats.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003 Nov;14(11):2833-42. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000095248.91994.d3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 14569093
-
[Molecular mechanisms of nephro-protective action of enalapril in experimental chronic renal failure].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999;Suppl 52:1-93. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999. PMID: 10589103 Review. Polish.
-
Hyperfiltration and diabetic nephropathy: is it the beginning? Or is it the end?Semin Nephrol. 1990 May;10(3):228-41. Semin Nephrol. 1990. PMID: 2190280 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperglycemia activates the renin-angiotensin system and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidneys.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2018 Jul-Sep;19(3):1470320318803009. doi: 10.1177/1470320318803009. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2018. PMID: 30264671 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Oct;60(5):443-449. doi: 10.1590/2359-3997000000188. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27812607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advani A, Huang Q, Thai K, Advani SL, White KE, Kelly DJ, Yuen DA, Connelly KA, Marsden PA, Gilbert RE. Long-term administration of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat attenuates renal injury in experimental diabetes through an endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:2205–2214. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Lee KE, Cruickshanks KJ, Moss SE. The incidence of hypertension in insulin-dependent diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:622–627. - PubMed
-
- Ueda H, Ishimura E, Shoji T, Emoto M, Morioka T, Matsumoto N, Fukumoto S, Miki T, Inaba M, Nishizawa Y. Factors affecting progression of renal failure in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1530–1534. - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–869. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

