Systematic review and cost-benefit analysis of radial artery access for coronary angiography and intervention
- PMID: 22740010
- PMCID: PMC3430729
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.112.965269
Systematic review and cost-benefit analysis of radial artery access for coronary angiography and intervention
Abstract
Background: Radial artery access for coronary angiography and interventions has been promoted for reducing hemostasis time and vascular complications compared with femoral access, yet it can take longer to perform and is not always successful, leading to concerns about its cost. We report a cost-benefit analysis of radial catheterization based on results from a systematic review of published randomized controlled trials.
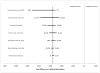
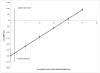
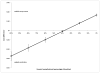
Methods and results: The systematic review added 5 additional randomized controlled trials to a prior review, for a total of 14 studies. Meta-analyses, following Cochrane procedures, suggested that radial catheterization significantly increased catheterization failure (OR, 4.92; 95% CI, 2.69-8.98), but reduced major complications (OR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.24-0.42), major bleeding (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.27-0.57), and hematoma (OR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.27-0.48) compared with femoral catheterization. It added approximately 1.4 minutes to procedure time (95% CI, -0.22 to 2.97) and reduced hemostasis time by approximately 13 minutes (95% CI, -2.30 to -23.90). There were no differences in procedure success rates or major adverse cardiovascular events. A stochastic simulation model of per-case costs took into account procedure and hemostasis time, costs of repeating the catheterization at the alternate site if the first catheterization failed, and the inpatient hospital costs associated with complications from the procedure. Using base-case estimates based on our meta-analysis results, we found the radial approach cost $275 (95% CI, -$374 to -$183) less per patient from the hospital perspective. Radial catheterization was favored over femoral catheterization under all conditions tested.
Conclusions: Radial catheterization was favored over femoral catheterization in our cost-benefit analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Rao SV, Ou FS, Wang TY, Roe MT, Brindis R, Rumsfeld JS, Peterson ED. Trends in the prevalence and outcomes of radial and femoral approaches to percutaneous coronary intervention: a report from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;1:379–386. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand OF, Rao SV, Pancholy S, Jolly SS, Rodes-Cabau J, Larose E, Costerousse O, Harmon M, Mann T. Transradial approach for coronary angiography and interventions: results of the first international transradial practice survey. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:1022–1031. - PubMed
-
- Jolly SS, Amlani S, Hamon M, Yusuf S, Mehta SR. Radial versus femoral access for coronary angiography or intervention and the impact on major bleeding and ischemic events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am Heart J. 2009;157:132–140. - PubMed
-
- Fearon WF, Bornschein B, Tonino PA, Gothe RM, Bruyne BD, Pijls NH, Siebert U Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME) Study Investigators. Economic evaluation of fractional flow reserve-guided percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with multivessel disease. Circulation. 2010;122:2545–2450. - PubMed
-
- Pinto DS, Stone GW, Shi C, Dunn ES, Reynolds MR, York M, Walczak J, Berezin RH, Mehran R, McLaurin BT, Cox DA, Ohman EM, Lincoff AM, Cohen DJ ACUITY (Acute Catheterization and Urgent Intervention Triage Strategy) Investigators. Economic evaluation of bivalirudin with or without glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibition versus heparin with routine glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibition for early invasive management of acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1758–1768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

