Degradation of mRNAs that lack a stop codon: a decade of nonstop progress
- PMID: 22740367
- PMCID: PMC3638749
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1124
Degradation of mRNAs that lack a stop codon: a decade of nonstop progress
Abstract
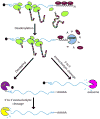
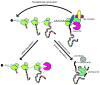
Nonstop decay is the mechanism of identifying and disposing aberrant transcripts that lack in-frame stop codons. It is hypothesized that these transcripts are identified during translation when the ribosome arrives at the 3' end of the mRNA and stalls. Presumably, the ribosome stalling recruits additional cofactors, Ski7 and the exosome complex. The exosome degrades the transcript using either one of its ribonucleolytic activities, and the ribosome and the peptide are both released. Additional precautionary measures by the nonstop decay pathway may include translational repression of the nonstop transcript after translation, and proteolysis of the released peptide by the proteasome. This surveillance mechanism protects the cells from potentially harmful truncated proteins, but it may also be involved in mediating critical cellular functions of transcripts that are prone to stop codon read-through. Important advances have been made in the past decade as we learn that nonstop decay may have implications in human disease.
Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Meyer S, Temme C, Wahle E. Messenger RNA turnover in eukaryotes: pathways and enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;39:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Muhlrad D, Decker CJ, Parker R. Deadenylation of the unstable mRNA encoded by the yeast MFA2 gene leads to decapping followed by 5′->3′ digestion of the transcript. Genes Dev. 1994;8:855–866. - PubMed
-
- Shyu AB, Belasco JG, Greenberg ME. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991;5:221–231. - PubMed
-
- Muhlrad D, Parker R. Mutations affecting stability and deadenylation of the yeast MFA2 transcript. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2100–2111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous