HTLV-1 tax-induced rapid senescence is driven by the transcriptional activity of NF-κB and depends on chronically activated IKKα and p65/RelA
- PMID: 22740410
- PMCID: PMC3416137
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00158-12
HTLV-1 tax-induced rapid senescence is driven by the transcriptional activity of NF-κB and depends on chronically activated IKKα and p65/RelA
Abstract
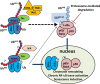
The HTLV-1 oncoprotein Tax is a potent activator of classical and alternative NF-κB pathways and is thought to promote cell proliferation and transformation via NF-κB activation. We showed recently that hyperactivation of NF-κB by Tax triggers a cellular senescence response (H. Zhi et al., PLoS Pathog. 7:e1002025, 2011). Inhibition of NF-κB activation by expression of I-κBα superrepressor or by small hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown of p65/RelA rescues cells from Tax-induced rapid senescence (Tax-IRS). Here we demonstrate that Tax-IRS is driven by the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. Knockdown of IKKγ, the primary Tax target, by shRNAs abrogated Tax-mediated activation of both classical and alternative NF-κB pathways and rendered knockdown cells resistant to Tax-IRS. Consistent with a critical role of IKKα in the transcriptional activity of NF-κB, IKKα deficiency drastically decreased NF-κB trans-activation by Tax, although it only modestly reduced Tax-mediated I-κBα degradation and NF-κB nuclear localization. In contrast, although IKKβ knockdown attenuated Tax-induced NF-κB transcriptional activation, the residual NF-κB activation in IKKβ-deficient cells was sufficient to trigger Tax-IRS. Importantly, the phenotypes of NIK and TAK1 knockdown were similar to those of IKKα and IKKβ knockdown, respectively. Finally, double knockdown of RelB and p100 had a minor effect on senescence induction by Tax. These data suggest that Tax, through its interaction with IKKγ, helps recruit NIK and TAK1 for IKKα and IKKβ activation, respectively. In the presence of Tax, the delineation between the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways becomes obscured. The senescence checkpoint triggered by Tax is driven by the transcriptional activity of NF-κB, which depends on activated IKKα and p65/RelA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax induction of NF-kappaB involves activation of the IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) and IKKbeta cellular kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Sep;18(9):5157-65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.9.5157. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9710600 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-to-gene coordinated regulation of transcription and alternative splicing by 3D chromatin remodeling upon NF-κB activation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 28;52(4):1527-1543. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae015. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38272542 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 Tax is a critical lipid raft modulator that hijacks IkappaB kinases to the microdomains for persistent activation of NF-kappaB.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 6;284(10):6208-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806390200. Epub 2009 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19129196
-
Activation of I-kappaB kinase by the HTLV type 1 Tax protein: mechanistic insights into the adaptor function of IKKgamma.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Nov 1;16(16):1591-6. doi: 10.1089/08892220050193001. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11080796 Review.
-
Move or die: the fate of the Tax oncoprotein of HTLV-1.Viruses. 2011 Jun;3(6):829-57. doi: 10.3390/v3060829. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the CDK7 Gene, Coding for the Catalytic Subunit of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK)-Activating Kinase (CAK) and General Transcription Factor II H, by the Trans-Activator Protein Tax of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type-1.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;15(8):1080. doi: 10.3390/genes15081080. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202439 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on the Metabolic Landscape of Oncogenic Viruses.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;14(23):5742. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235742. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Tax Stimulates Ubiquitin E3 Ligase, Ring Finger Protein 8, to Assemble Lysine 63-Linked Polyubiquitin Chains for TAK1 and IKK Activation.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Aug 18;11(8):e1005102. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005102. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26285145 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-Activation of the Coactivator-Associated Arginine Methyltransferase 1 (Carm1) Gene by the Oncogene Product Tax of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1.Genes (Basel). 2024 May 27;15(6):698. doi: 10.3390/genes15060698. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927636 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB signaling mechanisms in HTLV-1-induced adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(18):3324-3336. doi: 10.1111/febs.14492. Epub 2018 May 14. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29722927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anest V, et al. 2003. A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature 423:659–663 - PubMed
-
- Carter RS, Pennington KN, Arrate P, Oltz EM, Ballard DW. 2005. Site-specific monoubiquitination of IkappaB kinase IKKbeta regulates its phosphorylation and persistent activation. J. Biol. Chem. 280:43272–43279 - PubMed
-
- Chu ZL, Shin YA, Yang JM, Di Donato JA, Ballard LHDW. 1999. IKKgamma mediates the interaction of cellular IkappaB kinases with the tax transforming protein of human T cell leukemia virus type 1. J. Biol. Chem. 274:15297–15300 - PubMed
-
- Claudio E, Brown K, Park S, Wang H, Siebenlist U. 2002. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-kappa B2 in maturing B cells. Nat. Immunol. 3:958–965 - PubMed
-
- Dejardin E, et al. 2002. The lymphotoxin-beta receptor induces different patterns of gene expression via two NF-kappaB pathways. Immunity 17:525–535 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

