Separation of proteins from human plasma by sample displacement chromatography in hydrophobic interaction mode
- PMID: 22740472
- PMCID: PMC3807253
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201200006
Separation of proteins from human plasma by sample displacement chromatography in hydrophobic interaction mode
Abstract
Sample displacement chromatography (SDC) in reversed-phase and ion-exchange modes was introduced approximately 20 years ago. This method was first used for the preparative purification of peptides and proteins. Recently, SDC in ion-exchange mode was also successfully used for enrichment of low-abundance proteins from human plasma. In this paper, the use of SDC for the separation of plasma proteins in hydrophobic interaction mode is demonstrated. By use of two or more columns coupled in series during sample application, and subsequent elution of detached columns in parallel, additional separation of bound proteins was achieved. Further low-abundance, physiologically active proteins could be highly enriched and detected by ESI-MS/MS.
© 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


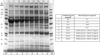
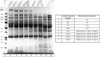


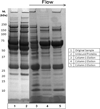

References
-
- Hodges RS, Burke TWL, Mant CT. J. Chromatogr. A. 1988;444:349–362. - PubMed
-
- Lorne Burke TWL, Mant CT, Hodges RS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1988;11:1229–1247.
-
- Veeraragavan K, Bernier A, Braendli E. J. Chromatogr. A. 1991;541:207–220.
-
- Husband DL, Mant CT, Hodges RS. J. Chromatogr. A. 2000;893:81–94. - PubMed
-
- Mant CT, Hodges RS. J. Chromatogr. A. 2002;972:101–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

