Overexpression of IL-32 is a novel prognostic factor in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 22740938
- PMCID: PMC3362389
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2011.511
Overexpression of IL-32 is a novel prognostic factor in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
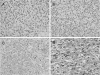
Interleukin-32 (IL-32) is a proinflammatory cytokine that acts as a significant pathogenetic factor in various diseases and malignancies. However, the clinical effect of IL-32 expression in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has not previously been investigated. The aim of the present study was to examine the significance of IL-32 overexpression in localized clear cell RCC (CCRCC). We examined 112 patients with localized CCRCC who underwent nephrectomy. The clinicopathological data were obtained by retrospective review and the expression levels of IL-32 were studied by immunohistochemistry. Tumors were classified according to staining intensity (0, no staining intensity; 1, weak; 2, intermediate; 3, strong). The cases with staining intensities from 0 to 2 comprised the IL-32 low-expression group (LEG), whereas those with a staining intensity of 3 comprised the IL-32 high-expression group (HEG). Correlations between IL-32 expression and clinicopathological parameters were determined. Staining intensities were determined for all cases as follows: 26 cases (23.2%) (score 0), 43 cases (38.4%) (score 1), 31 cases (27.7%) (score 2) and 12 cases (10.7%) (score 3). IL-32 HEG exhibited a higher recurrence rate compared to the IL-32 LEG (50 vs. 13%, P=0.001). For survival rates, the 5-year recurrence-free survival (RFS), disease-specific survival (DSS) and overall survival (OS) rates were lower in the IL-32 HEG group compared with the IL-32 LEG group (RFS, P=0.001; DSS, P<0.001; OS, P=0.026, respectively). Univariate analyses revealed that Fuhrman nuclear grade and a high IL-32 expression were significant prognostic factors for predicting RFS, DSS and OS in CCRCC, whereas multivariate analyses indicated that Fuhrman nuclear grade and high IL-32 expression were still independent risk factors. In conclusion, IL-32 overexpression was associated with high recurrence rates and low RFS, DSS and OS, indicating that it may be a novel prognostic factor for predicting outcomes in patients with CCRCC.
Figures
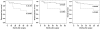
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Wieder J, et al. Risk group assessment and clinical outcome algorithm to predict the natural history of patients with surgically resected renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4559–4566. - PubMed
-
- Phuoc NB, Ehara H, Gotoh T, et al. Prognostic value of the co-expression of carbonic anhydrase IX and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008;20:525–530. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
