TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and glioma risk: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 22740959
- PMCID: PMC3362515
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2011.521
TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and glioma risk: A meta-analysis
Abstract
TP53 codon 72 polymorphism has been reported to affect regulatory networks central to glioma development. Although a number of published studies noted the association between TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and glioma risk, their conclusions were inconsistent. A meta-analysis was used to assess the possible association between TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and glioma risk. The PubMed databases were searched, relevant articles were identified and data were retrieved based on the inclusion criteria. The odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were determined on the pooled dataset. We retrieved eight different studies including 2,260 glioma cases and 3,506 controls. However, no association was found between the TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and glioma risk regarding the comparison between glioma cases and the controls. By further stratification based on criteria such as tumor grade, and the geographical location of the patients and the relevant controls, we found a significant association in the subgroup of patients with high-grade glioma in Europeans compared to controls in two models of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism, which include the dominant model [C/C + G/C vs. G/G: OR=1.35, 95% CI (1.14, 1.59), P=0.0005, P(h)=0.13] and the additive model [C allele vs. G allele: OR=1.16, 95% CI (1.02, 1.33), P=0.03, P(h)=0.37]. Our analysis suggests that TP53 codon 72 polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of high-grade glioma development in Europeans.
Figures
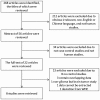
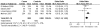
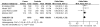


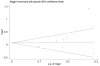

Similar articles
-
TP53 codon 72 Polymorphism and bladder cancer risk: a meta-analysis and emphasis on the role of tumor or smoking status.J Cancer. 2018 Sep 8;9(19):3522-3531. doi: 10.7150/jca.26264. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30310509 Free PMC article.
-
The TP53 codon 72 Pro/Pro genotype may be associated with an increased lung cancer risk in North China: an updated meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Mar 15;8(3):3120-6. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26064201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between TP53 Gene Codon 72 Polymorphism and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Susceptibility: Evidence Based on a Meta-Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Oct 9;21:3048-53. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894625. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26451982 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the codon 72 polymorphism of the TP53 gene and the risk of recurrent implantation failure.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016 Feb;42(2):184-9. doi: 10.1111/jog.12867. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016. PMID: 26555776
-
Association between the p53 codon 72 polymorphism and primary open-angle glaucoma risk: Meta-analysis based on 11 case-control studies.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;64(10):756-761. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.195002. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27905339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Model and Nomogram Construction and Validation With an Autophagy-Related Gene Signature in Low-Grade Gliomas.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 18;13:905751. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.905751. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35923699 Free PMC article.
-
Low penetrance susceptibility to glioma is caused by the TP53 variant rs78378222.Br J Cancer. 2013 May 28;108(10):2178-85. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.155. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23571737 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive capability of immunohistochemistry and DNA sequencing for determining TP53 functional mutation status: a comparative study of 41 glioblastoma patients.Oncotarget. 2019 Oct 22;10(58):6204-6218. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27252. eCollection 2019 Oct 22. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31692772 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Genetic Risk Prediction of Subsequent CNS Tumors in Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Report From the COG ALTE03N1 Study.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Nov 10;35(32):3688-3696. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.7444. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28976792 Free PMC article.
-
No evidence of correlation between p53 codon 72 G > C gene polymorphism and cancer risk in Indian population: a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Sep;35(9):8607-13. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2114-7. Epub 2014 May 28. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24863946
References
-
- Rickert CH, Paulus W. Epidemiology of central nervous system tumors in childhood and adolescence based on the new WHO classification. Childs Nerv Syst. 2001;17:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 2000;408:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Phatak P, Selvi SK, Divya T, Hegde AS, Hegde S, Somasundaram K. Alterations in tumour suppressor gene p53 in human gliomas from Indian patients. J Biosci. 2000;27:673–678. - PubMed
-
- Olivier M, Eeles R, Hollstein M, Khan MA, Harris CC, Hainaut P. The IARC TP53 database: new online mutation analysis and recommendations to users. Hum Mut. 2002;19:607–614. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
