Serum IGFBP-3 is a more effective predictor than IGF-1 and IGF-2 for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HCV infection
- PMID: 22740980
- PMCID: PMC3362503
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2011.546
Serum IGFBP-3 is a more effective predictor than IGF-1 and IGF-2 for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HCV infection
Abstract
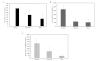
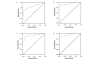
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) contributes to 14.8% of all cancer mortality in Egypt, which has a high prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV). We have previously shown alterations in the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor signalling pathway during experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. The aim of this study was to determine whether serum levels of IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFBP-3 can be used to discriminate between HCC and the stages of hepatic dysfunction in patients with liver cirrhosis assessed by the Child-Pugh (CP) score, and to correlate these levels with HCC stages. We recruited 241 subjects to the present study; 79 with liver cirrhosis, 62 with HCV-induced HCC and 100 age-matched controls. Results showed that serum levels of IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFBP-3 were reduced significantly in cirrhosis and HCC patients in comparison to the controls, and that this reduction negatively correlated with the CP scores. However, only IGFBP-3 levels showed significant negative correlation with α-fetoprotein levels. The reduction in IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 but not IGF-2 levels was significant in HCC in comparison to patients with cirrhosis. None of the parameters significantly correlated with the HCC stage. IGFBP-3 levels discriminated between cirrhosis and HCC at a sensitivity of 87%, a specificity of 80% and a cut-off value of <682.6 ng/ml. In conclusion, although our results showed that serum IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFBP-3 are reduced with the progression of hepatic dysfunction, only IGFBP-3 may be considered as the most promising serological marker for the prediction of the development of HCC in the chronic HCV patients with liver cirrhosis.
Figures

References
-
- Anwar WA, Khaled HM, Amra HA, El-Nezami H, Loffredo CA. Changing pattern of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its risk factors in Egypt: possibilities for prevention. Mutat Res. 2008;659:176–184. - PubMed
-
- Sievert W, Altraif I, Razavi HA, et al. A systematic review of hepatitis C virus epidemiology in Asia, Australia and Egypt. Liver Int. 2011;31(Suppl 2):61–80. - PubMed
-
- Thorgeirsson SS, Grisham JW. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Furstenberger G, Senn HJ. Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:298–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
