Serum amyloid A: A new potential serum marker correlated with the stage of breast cancer
- PMID: 22741023
- PMCID: PMC3362442
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.584
Serum amyloid A: A new potential serum marker correlated with the stage of breast cancer
Abstract
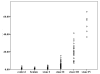
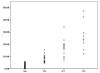
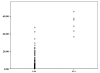
Previous studies reported that serum amyloid A (SAA) is elevated in patients with tumors, including breast cancer, compared to healthy controls. In addition, the levels of SAA increase gradually with tumor progression. In this study, we investigated the blood SAA level of breast cancer patients, and evaluated its potential as a serum biomarker for the early diagnosis of breast cancer and as a staging estimate. SAA protein was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in serum samples from 30 healthy women, 21 women with benign diseases and 118 breast cancer patients who were subdivided into 4 groups based on their clinical characteristics. SAA levels were not statistically different in stage I breast cancer patients compared with the healthy controls and benign breast disease patients. SAA concentrations had medians of 0.63 µg/ml in normal healthy women, 0.76 µg/ml in patients with benign disease (p>0.05) and 0.82 µg/ml in stage I breast cancer patients (p>0.05). By contrast, SAA values in stage Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ patients had a significantly higher median compared to those of the healthy, benign breast diseases and stage I groups (p<0.05). Breast cancer patients with lymph node (LN) metastasis or distant metastasis were found to have significantly higher SAA concentrations than those without metastases. SAA is not a suitable marker for early breast cancer diagnosis, but its level is correlated with the stage of breast cancer. Thus, it may be a good candidate marker for the staging and prognosis of breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Veronesi U, Boyle P, Goldhirsch A, Orecchia R, Viale G. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2005;365:1727–1741. - PubMed
-
- Redondo M, Rivas-Ruiz F, Guzman-Soler MC, Labajos C. Monitoring indicators of health care quality by means of a hospital register of tumours. J Eval Clin Pract. 2008;14:1026–1030. - PubMed
-
- Tabar L, Yen MF, Vitak B, Chen HH, Smith RA, Duffy SW. Mammography service screening and mortality in breast cancer patients: 20-year follow-up before and after introduction of screening. Lancet. 2003;361:1405–1410. - PubMed
-
- Ding J, Warren R, Warsi I. et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of using standard mammogram form to predict breast cancer risk: case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:1074–1081. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
