A case of clonorchiasis with focal intrahepatic duct dilatation mimicking an intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 22741114
- PMCID: PMC3363046
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2011.44.1.55
A case of clonorchiasis with focal intrahepatic duct dilatation mimicking an intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
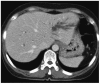
Biliary strictures can be caused by various diseases. Intrahepatic duct (IHD) strictures are usually related to IHD stones and cholangitis. However, focal IHD strictures without IHD stones often create diagnostic problems. Parasitic diseases such as clonorchiasis can be a rare cause of an IHD stricture. Human clonorchiasis (Clonorchis sinensis infection) is an endemic parasitic disease in Eastern Asia, including Korea, and patients acquire the infestation by eating raw fish. On radiological examinations, clonorchiasis shows typically diffuse, minimal, or mild dilatation of the small IHD, particularly in the periphery, without dilatation of the extrahepatic duct. However, diagnosis of clonorchiasis can sometimes be difficult when radiological changes are atypical. We report a case of focal left IHD dilatation caused by clonorchiasis that was confused with a malignancy.
Keywords: Clonorchiasis; Dilatation; Intrahepatic bile duct; Stricture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Seo DW, Kim MH, Lee SK, et al. Usefulness of cholangioscopy in patients with focal stricture of the intrahepatic duct unrelated to intrahepatic stones. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:204–209. - PubMed
-
- Yeh YH, Huang MH, Yang JC, Mo LR, Lin J, Yueh SK. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy and lithotripsy in the treatment of intrahepatic stones: a study with 5 year follow-up. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995;42:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Joo CY, Chung MS, Kim SJ, Kang CM. Changing patterns of Clonorchis sinensis infections in Kyongbuk, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1997;35:155–164. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

