International live endoscopic multichannel demonstration using superfast broadband internet connections
- PMID: 22741135
- PMCID: PMC3363122
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.1.73
International live endoscopic multichannel demonstration using superfast broadband internet connections
Abstract
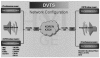
Background/aims: Telemedicine is a convenient and efficient tool for remote education in various fields. The telemedicine system can also be used to educate doctors and medical students. The aim of our study was to establish the effectiveness of the telemedical system for use in a live endoscopic multichannel demonstration conference and to test the effectiveness and usefulness of a multicenter-based live endoscopic demonstration through live, interactive, high resolution video transmission using advanced networks and the digital video transport system (DVTS).
Methods: This study is a prospective multicenter pilot study. A live demonstration of an endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) using advanced network technology was performed.
Results: The DVTS successfully transmitted uncompressed, high-resolution, digital lectures with endoscopy video during a multichannel endoscopic live demonstration of ESD and ERCP over multiple advanced networks. The overall satisfaction rating when the endoscopic lecture demonstration was performed by combining DVTS was generally good.
Conclusions: We believe that a multicenter-based live endoscopic demonstration is a very effective conferencing method when using advanced networks and DVTS.
Keywords: International educational exchange; Internet; Telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures





Comment in
-
Live endoscopy demonstration using superfast broadband internet connections: the future of medical education and conferences.Clin Endosc. 2012 Mar;45(1):1. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.1.1. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Clin Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22741127 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Harris BA., Jr Telemedicine: a glance into the future. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994;69:1212–1214. - PubMed
-
- Hahm JS, Lee HL, Kim SI, et al. A remote educational system in medicine using digital video. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54:373–376. - PubMed
-
- Hahm JS, Shimizu S, Nakashima N, et al. Telemedicine with digital video transport system. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004;43:370–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

