Minimal requirements for inhibition of MraY by lysis protein E from bacteriophage ΦX174
- PMID: 22742425
- PMCID: PMC3429702
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08153.x
Minimal requirements for inhibition of MraY by lysis protein E from bacteriophage ΦX174
Abstract
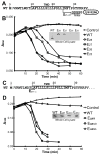
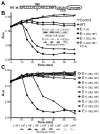
The DNA phage ΦX174 encodes the integral membrane protein E whose expression leads to host cell lysis by inhibition of the peptidoglycan synthesis enzyme MraY. Here we use mutagenesis to characterize the molecular details of the E lysis mechanism. We find that a minimal 18-residue region with the modified wild-type sequences of the conserved transmembrane helix of E is sufficient to lyse host cells and that specific residues within and at the boundaries of this helix are important for activity. This suggests that positioning of the helix in the membrane is critical for interactions with MraY. We further characterize the interaction site of the transmembrane helix with MraY demonstrating E forms a stable complex with MraY. Triggering cell lysis by peptidoglycan synthesis inhibition is a traditional route for antimicrobial strategies. Understanding the mechanism of bacterial cell lysis by E will provide insights into new antimicrobial strategies using re-engineered E peptides.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interaction of the transmembrane domain of lysis protein E from bacteriophage phiX174 with bacterial translocase MraY and peptidyl-prolyl isomerase SlyD.Microbiology (Reading). 2006 Oct;152(Pt 10):2959-2967. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28776-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2006. PMID: 17005977
-
Genetic analysis of MraY inhibition by the phiX174 protein E.Genetics. 2008 Nov;180(3):1459-66. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.093443. Epub 2008 Sep 14. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18791230 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel inhibition site in translocase MraY based upon the site of interaction with lysis protein E from bacteriophage ϕX174.Chembiochem. 2014 Jun 16;15(9):1300-8. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201402064. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 24895118
-
Inhibition of phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase (MraY) by nucleoside natural product antibiotics, bacteriophage ϕX174 lysis protein E, and cationic antibacterial peptides.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Dec 15;24(24):6340-6347. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27021004 Review.
-
Phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase (MraY) as a target for antibacterial agents and antibacterial proteins.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Jun;6(2):85-106. doi: 10.2174/187152606784112128. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16789873 Review.
Cited by
-
Phage single-gene lysis: Finding the weak spot in the bacterial cell wall.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 8;294(10):3350-3358. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.001773. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30420429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Re-directing bacterial microcompartment systems to enhance recombinant expression of lysis protein E from bacteriophage ϕX174 in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Apr 26;16(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0685-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28446197 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed lysis confers resistance to the nucleoside analogue 5-fluorouracil and alleviates mutation accumulation in the single-stranded DNA bacteriophage ϕX174.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):5042-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02147-13. Epub 2014 Feb 19. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24554658 Free PMC article.
-
The Membrane Steps of Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis as Antibiotic Targets.Antibiotics (Basel). 2016 Aug 26;5(3):28. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics5030028. Antibiotics (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27571111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autotransporter-based antigen display in bacterial ghosts.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Jan;81(2):726-35. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02733-14. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25398861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson H, Bakker E, von Heijne G. Different positively charged amino acids have similar effects on the topology of a polytopic transmembrane protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:1491–1495. - PubMed
-
- Bergh O, Borsheim KY, Bratbak G, Heldal M. High abundance of viruses found in aquatic environments. Nature. 1989;340:467–468. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt TG, Roof WD, Young R. The Escherichia coli FKBP-type PPIase SlyD is required for the stabilization of the E lysis protein of bacteriophage phi X174. Mol Microbiol. 2002a;45:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt TG, Struck DK, Young R. The lysis protein E of phi X174 is a specific inhibitor of the MraY-catalyzed step in peptidoglycan synthesis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:6093–6097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

