High density diffusion-free nanowell arrays
- PMID: 22742968
- PMCID: PMC3412896
- DOI: 10.1021/pr300467q
High density diffusion-free nanowell arrays
Abstract
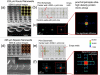
Proteomics aspires to elucidate the functions of all proteins. Protein microarrays provide an important step by enabling high-throughput studies of displayed proteins. However, many functional assays of proteins include untethered intermediates or products, which could frustrate the use of planar arrays at very high densities because of diffusion to neighboring features. The nucleic acid programmable protein array (NAPPA) is a robust in situ synthesis method for producing functional proteins just-in-time, which includes steps with diffusible intermediates. We determined that diffusion of expressed proteins led to cross-binding at neighboring spots at very high densities with reduced interspot spacing. To address this limitation, we have developed an innovative platform using photolithographically etched discrete silicon nanowells and used NAPPA as a test case. This arrested protein diffusion and cross-binding. We present confined high density protein expression and display, as well as functional protein-protein interactions, in 8000 nanowell arrays. This is the highest density of individual proteins in nanovessels demonstrated on a single slide. We further present proof of principle results on ultrahigh density protein arrays capable of up to 24000 nanowells on a single slide.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson KS, Sibani S, Wallstrom G, Qiu J, Mendoza EA, Raphael J, Hainsworth E, Montor WR, Wong J, Park JG, Lokko N, Logvinenko T, Ramachandran N, Godwin AK, Marks J, Engstrom P, Labaer J. Protein microarray signature of autoantibody biomarkers for the early detection of breast cancer. J Proteome Res. 10(1):85–96. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones RB, Gordus A, Krall JA, MacBeath G. A quantitative protein interaction network for the ErbB receptors using protein microarrays. Nature. 2006;439(7073):168–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

