Both internalization and AIP1 association are required for tumor necrosis factor receptor 2-mediated JNK signaling
- PMID: 22743059
- PMCID: PMC3421067
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.253666
Both internalization and AIP1 association are required for tumor necrosis factor receptor 2-mediated JNK signaling
Abstract
Objective: The proinflammtory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF), primarily via TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1), induces nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent cell survival, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and caspase-dependent cell death, regulating vascular endothelial cell (EC) activation and apoptosis. However, signaling by the second receptor, TNFR2, is poorly understood. The goal of this study was to dissect how TNFR2 mediates NF-κB and JNK signaling in vascular EC, and its relevance to in vivo EC function.
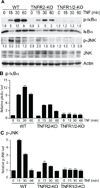
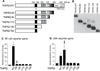
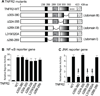
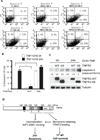
Methods and results: We show that TNFR2 contributes to TNF-induced NF-κB and JNK signaling in EC as TNFR2 deletion or knockdown reduces the TNF responses. To dissect the critical domains of TNFR2 that mediate the TNF responses, we examine the activity of TNFR2 mutant with a specific deletion of the TNFR2 intracellular region, which contains conserved domain I, domain II, domain III, and 2 TNFR-associated factor-2-binding sites. Deletion analyses indicate that different sequences on TNFR2 have distinct roles in NF-κB and JNK activation. Specifically, deletion of the TNFR-associated factor-2-binding sites (TNFR2-59) diminishes the TNFR2-mediated NF-κB, but not JNK activation; whereas, deletion of domain II or domain III blunts TNFR2-mediated JNK but not NF-κB activation. Interestingly, we find that the TNFR-associated factor-2-binding sites ensure TNFR2 on the plasma membrane, but the di-leucine LL motif within the domain II and aa338-355 within the domain III are required for TNFR2 internalization as well as TNFR2-dependent JNK signaling. Moreover, domain III of TNFR2 is responsible for association with ASK1-interacting protein-1, a signaling adaptor critical for TNF-induced JNK signaling. While TNFR2 containing the TNFR-associated factor-2-binding sites prevents EC cell death, a specific activation of JNK without NF-κB activation by TNFR2-59 strongly induces caspase activation and EC apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our data reveal that both internalization and ASK1-interacting protein-1 association are required for TNFR2-dependent JNK and apoptotic signaling. Controlling TNFR2-mediated JNK and apoptotic signaling in EC may provide a novel strategy for the treatment of vascular diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AIP1/DAB2IP, a novel member of the Ras-GAP family, transduces TRAF2-induced ASK1-JNK activation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 22;279(43):44955-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407617200. Epub 2004 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15310755
-
TNFR2 increases the sensitivity of ligand-induced activation of the p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways and signals TRAF2 protein degradation in macrophages.Cell Signal. 2014 Apr;26(4):683-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.12.009. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24378531
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) signaling is negatively regulated by a novel, carboxyl-terminal TNFR-associated factor 2 (TRAF2)-binding site.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31572-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504849200. Epub 2005 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16020544
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
-
Mechanisms of crosstalk between TNF-induced NF-kappaB and JNK activation in hepatocytes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 30;72(9):1090-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.003. Epub 2006 Aug 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16934229 Review.
Cited by
-
AIP1-mediated stress signaling in atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015 May;17(5):503. doi: 10.1007/s11883-015-0503-z. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015. PMID: 25732743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2: its contribution to acute cellular rejection and clear cell renal carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:821310. doi: 10.1155/2013/821310. Epub 2013 Nov 17. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24350291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting TNFR2 for cancer immunotherapy: recent advances and future directions.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 2;22(1):812. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05620-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39223671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Signaling Pathway of TNF Receptors: Linking Animal Models of Renal Disease to Human CKD.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 18;23(6):3284. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063284. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of DAB2IP Inhibits Ras Activity and Tumorigenesis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033819895494. doi: 10.1177/1533033819895494. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32336215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pober JS, Min W. Endothelial cell dysfunction, injury and death. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006:135–156. - PubMed
-
- Pober JS, Min W, Bradley JR. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction, Injury, and Death. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:71–95. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
-
- Fiers W, Beyaert R, Boone E, Cornelis S, Declercq W, Decoster E, Denecker G, Depuydt B, De Valck D, De Wilde G, Goossens V, Grooten J, Haegeman G, Heyninck K, Penning L, Plaisance S, Vancompernolle K, Van Criekinge W, Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe W, Van de Craen M, Vandevoorde V, Vercammen D. TNF-induced intracellular signaling leading to gene induction or to cytotoxicity by necrosis or by apoptosis. J Inflamm. 1995;47:67–75. - PubMed
-
- Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP. Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:331–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

