MIRD pamphlet No. 23: quantitative SPECT for patient-specific 3-dimensional dosimetry in internal radionuclide therapy
- PMID: 22743252
- PMCID: PMC3465844
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.111.100123
MIRD pamphlet No. 23: quantitative SPECT for patient-specific 3-dimensional dosimetry in internal radionuclide therapy
Abstract
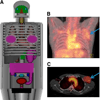
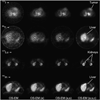
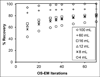
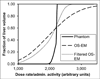
In internal radionuclide therapy, a growing interest in voxel-level estimates of tissue-absorbed dose has been driven by the desire to report radiobiologic quantities that account for the biologic consequences of both spatial and temporal nonuniformities in these dose estimates. This report presents an overview of 3-dimensional SPECT methods and requirements for internal dosimetry at both regional and voxel levels. Combined SPECT/CT image-based methods are emphasized, because the CT-derived anatomic information allows one to address multiple technical factors that affect SPECT quantification while facilitating the patient-specific voxel-level dosimetry calculation itself. SPECT imaging and reconstruction techniques for quantification in radionuclide therapy are not necessarily the same as those designed to optimize diagnostic imaging quality. The current overview is intended as an introduction to an upcoming series of MIRD pamphlets with detailed radionuclide-specific recommendations intended to provide best-practice SPECT quantification-based guidance for radionuclide dosimetry.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

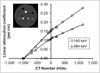
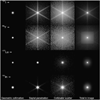
References
-
- International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) Absorbed-Dose Specification in Nuclear Medicine. Bethesda, MD: ICRU; 2002. Report 67.
-
- O’Donoghue JA. Implications of nonuniform tumor doses for radioimmunotherapy. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:1337–1341. - PubMed
-
- Dale RG. The application of the linear-quadratic dose-effect equation to fractionated and protracted radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1985;58:515–528. - PubMed
-
- Flux G, Bardiès M, Monsieurs M, Savolainen S, Strand SE, Lassmann M. The impact of PET and SPECT on dosimetry for targeted radionuclide therapy. Z Med Phys. 2006;16:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Siegel JA, Thomas SR, Stubbs JB, et al. MIRD pamphlet no. 16: techniques for quantitative radiopharmaceutical biodistribution data acquisition and analysis for use in human radiation dose estimates. J Nucl Med. 1999;40(suppl):37S–61S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
