Tenofovir in second-line ART in Zambia and South Africa: collaborative analysis of cohort studies
- PMID: 22743595
- PMCID: PMC3432418
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182632540
Tenofovir in second-line ART in Zambia and South Africa: collaborative analysis of cohort studies
Abstract
Objectives: Tenofovir (TDF) is increasingly used in second-line antiretroviral treatment (ART) in sub-Saharan Africa. We compared outcomes of second-line ART containing and not containing TDF in cohort studies from Zambia and the Republic of South Africa (RSA).
Methods: Patients aged 16 years and older starting protease-inhibitor-based second-line ART in Zambia (1 cohort) and RSA (5 cohorts) were included. We compared mortality, immunological failure (all cohorts), and virological failure (RSA only) between patients receiving and not receiving TDF. Competing risk models and Cox models adjusted for age, sex, CD4 count, time on first-line ART, and calendar year were used to analyze mortality and treatment failure, respectively. Hazard ratios (HRs) were combined in fixed-effects meta-analysis.
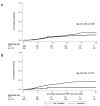
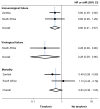
Findings: 1687 patients from Zambia and 1556 patients from RSA, including 1350 (80.0%) and 206 (13.2%) patients starting TDF, were followed over 4471 person-years. Patients on TDF were more likely to have started second-line ART in recent years and had slightly higher baseline CD4 counts than patients not on TDF. Overall, 127 patients died, 532 were lost to follow-up, and 240 patients developed immunological failure. In RSA, 94 patients had virologic failure. Combined HRs comparing TDF with other regimens were 0.60 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.41 to 0.87) for immunologic failure and 0.63 (0.38-1.05) for mortality. The HR for virologic failure in RSA was 0.28 (0.09-0.90).
Conclusions: In this observational study, patients on TDF-containing second-line ART were less likely to develop treatment failure than patients on other regimens. TDF seems to be an effective component of second-line ART in southern Africa.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tenofovir or zidovudine in second-line antiretroviral therapy after stavudine failure in southern Africa.Antivir Ther. 2014;19(5):521-5. doi: 10.3851/IMP2710. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Antivir Ther. 2014. PMID: 24296645 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of baseline renal function on tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy outcomes in Zambia.Clin Infect Dis. 2014 May;58(10):1473-80. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu117. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Clin Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24585558 Free PMC article.
-
Brief Report: Assessing the Association Between Changing NRTIs When Initiating Second-Line ART and Treatment Outcomes.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018 Apr 1;77(4):413-416. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001611. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018. PMID: 29206723 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor backbone on the efficacy of first-line boosted highly active antiretroviral therapy based on protease inhibitors: meta-regression analysis of 12 clinical trials in 5168 patients.HIV Med. 2009 Oct;10(9):527-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2009.00724.x. HIV Med. 2009. PMID: 19785663 Review.
-
Treatment failure and associated factors among people living with HIV on highly active antiretroviral therapy in mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 May 2;18(5):e0284405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284405. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37130123 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Loss to follow-up from antiretroviral therapy clinics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies in South Africa from 2011 to 2015.South Afr J HIV Med. 2019 Dec 18;20(1):984. doi: 10.4102/sajhivmed.v20i1.984. eCollection 2019. South Afr J HIV Med. 2019. PMID: 31956435 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of treatment failure on second-line antiretroviral therapy among adults in northwest Ethiopia: a multicentre retrospective follow-up study.BMJ Open. 2016 Dec 8;6(12):e012537. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012537. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27932339 Free PMC article.
-
How soon should patients be eligible for differentiated service delivery models for antiretroviral treatment? Evidence from a retrospective cohort study in Zambia.BMJ Open. 2022 Dec 22;12(12):e064070. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064070. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36549722 Free PMC article.
-
Time to Treatment Failure and Its Predictors Among Second-Line ART Clients in Amhara Region, Ethiopia: A Retrospective Follow-Up Study.HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2024 May 2;16:183-192. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S455885. eCollection 2024. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38711541 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Protease Inhibitor/Nucleos(t)ide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor-Based Second-line Antiretroviral Therapy for the Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Jun 1;66(12):1846-1857. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix1108. Clin Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29272346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Progress Report 2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. Towards universal access. Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector. Available at http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/2010progressreport/en/index.htm.
-
- Pujades-Rodriguez M, Balkan S, Arnould L, Brinkhof MA, Calmy A. Treatment failure and mortality factors in patients receiving second-line HIV therapy in resource-limited countries. JAMA. 2010 Jul 21;304(3):303–312. - PubMed
-
- Fox MP, Ive P, Long L, Maskew M, Sanne I. High rates of survival, immune reconstitution, and virologic suppression on second-line antiretroviral therapy in South Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010 Apr 1;53(4):500–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

