Enhanced anti-HIV efficacy of indinavir after inclusion in CD4-targeted lipid nanoparticles
- PMID: 22743598
- PMCID: PMC3551348
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182653c1f
Enhanced anti-HIV efficacy of indinavir after inclusion in CD4-targeted lipid nanoparticles
Abstract
Background: Combination drug therapy has reduced plasma HIV to undetectable levels; however, drug-sensitive virus persists in patients' lymphoid tissue. We have reported significant lymphoid tissue drug localization with indinavir-associated lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Our current objective is to evaluate whether additional enhancement is achievable by targeting these particles to CD4-HIV host cells.
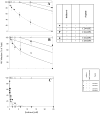
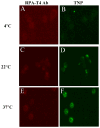
Methods: We characterized 2 peptide-coated (CD4-BP2 and CD4-BP4) drug-associated LNPs and demonstrated CD4-cell specificity. Drug-associated LNPs expressing polyethyleneglycol were exposed on HIV-2-infected cells under dynamic conditions that emulated lymph node physiology for 15, 30, and 60 minutes at concentrations from 0 to 25 μM and evaluated for antiviral activity and cell-associated drug concentrations. The specificity of CD4-mediated enhancement of indinavir LNPs antiviral activity was evaluated by blocking with anti-CD4 antibody.
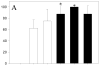
Results: Inclusion of CD4-binding peptides on LNPs enhanced antiviral activity for all incubation conditions, compared with control particles or soluble drug (eg, 60 minutes exposure, EC50 = 0.12-0.13 vs. 0.46 μM for targeted nanoparticles vs. soluble drug). The CD4-BP4 peptide exhibited higher efficiency in eliciting antiviral activity than CD4-BP2-coated particles (EC50 = 7.5 μM vs. >25 μM at 15 minutes drug exposure). This enhancement seems to be driven by CD4 availability and cell-associated indinavir concentrations, as blocking of CD4 significantly ablated indinavir efficacy in targeted particles and indinavir concentrations reflected the observed anti-HIV activity.
Conclusions: We constructed CD4-targeted LNPs that provide selective binding and efficient delivery of indinavir to CD4-HIV host cells. Inclusion of polyethyleneglycol in LNPs would minimize immune recognition of peptides. The enhancement of anti-HIV effects is effective even under limited time exposure.
Figures


References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. The New England journal of medicine. 1998 Mar 26;338(13):853–860. - PubMed
-
- Wong JK, Hezareh M, Gunthard HF, et al. Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science. 1997 Nov 14;278(5341):1291–1295. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz L, van Lunzen J, Arno A, et al. Protease inhibitor-containing regimens compared with nucleoside analogues alone in the suppression of persistent HIV-1 replication in lymphoid tissue. Aids. 1999 Jan 14;13(1):F1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

