An inhibitor of casein kinase 1 ε/δ partially normalizes the manic-like behaviors of the ClockΔ19 mouse
- PMID: 22743604
- PMCID: PMC3673712
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32835651fd
An inhibitor of casein kinase 1 ε/δ partially normalizes the manic-like behaviors of the ClockΔ19 mouse
Abstract
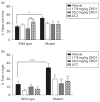
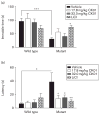
Bipolar disorder is a terrible and debilitating disease with limited treatment options. Circadian rhythm disruptions are prominent in bipolar subjects, and studies have shown that rhythm stabilization through psychosocial interventions can improve their symptoms. Furthermore, mice with a mutation in one of the central circadian proteins, CLOCK, have severely disrupted rhythms along with a behavioral profile that closely resembles human mania. A compound has been developed (CK01, similar to PF-670462) that inhibits the activity of casein kinase 1 (CK1), a critical protein involved in the timing of the molecular clock. Previous studies have shown that PF-670462 and other similar compounds are capable of entraining and stabilizing rhythms in arrhythmic animals. Here we show that chronic administration of CK01 leads to a reversal of the anxiety-related behavior, and partial reversal of the depression-related phenotypes of the Clock mutant mouse. This drug had no significant effects on the behavior of wild-type mice at the doses tested. These results suggest that CK1ε/δ inhibitors could be viable drugs for the treatment of bipolar disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Badura L, Swanson T, Adamowicz W, Adams J, Cianfrogna J, Fisher K, et al. An inhibitor of casein kinase I epsilon induces phase delays in circadian rhythms under free-running and entrained conditions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;322:730–738. - PubMed
-
- Davis M. The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:353–375. - PubMed
-
- Frank E, Swartz HA, Kupfer DJ. Interpersonal and social rhythm therapy: managing the chaos of bipolar disorder. Biolog psychiatry. 2000;48:593–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

