Exome sequencing identifies a novel multiple sclerosis susceptibility variant in the TYK2 gene
- PMID: 22744673
- PMCID: PMC3405256
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182616fc4
Exome sequencing identifies a novel multiple sclerosis susceptibility variant in the TYK2 gene
Abstract
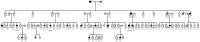
Objective: To identify rare variants contributing to multiple sclerosis (MS) susceptibility in a family we have previously reported with up to 15 individuals affected across 4 generations.
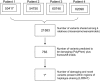
Methods: We performed exome sequencing in a subset of affected individuals to identify novel variants contributing to MS risk within this unique family. The candidate variant was genotyped in a validation cohort of 2,104 MS trio families.
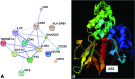
Results: Four family members with MS were sequenced and 21,583 variants were found to be shared among these individuals. Refining the variants to those with 1) a predicted loss of function and 2) present within regions of modest haplotype sharing identified 1 novel mutation (rs55762744) in the tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) gene. A different polymorphism within this gene has been shown to be protective in genome-wide association studies. In contrast, the TYK2 variant identified here is a novel, missense mutation and was found to be present in 10/14 (72%) cases and 28/60 (47%) of the unaffected family members. Genotyping additional 2,104 trio families showed the variant to be transmitted preferentially from heterozygous parents (transmitted 16: not transmitted 5; χ(2) = 5.76, p = 0.016).
Conclusions: Rs55762744 is a rare variant of modest effect on MS risk affecting a subset of patients (0.8%). Within this pedigree, rs55762744 is common and appears to be a modifier of modest risk effect. Exome sequencing is a quick and cost-effective method and we show here the utility of sequencing a few cases from a single, unique family to identify a novel variant. The sequencing of additional family members or other families may help identify other variants important in MS.
Figures
Comment in
-
Exome sequencing to find rare variants causing neurologic diseases.Neurology. 2012 Jul 31;79(5):396-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182617170. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Neurology. 2012. PMID: 22744653 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ascherio A, Munger KL. Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis: part I: the role of infection. Ann Neurol 2007; 61: 288– 299 . - PubMed
-
- Ascherio A, Munger KL. Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis: part II: noninfectious factors. Ann Neurol 2007; 61: 504– 513 . - PubMed
-
- Ebers GC, Koopman WJ, Hader W, et al. The natural history of multiple sclerosis: a geographically based study: 8: familial multiple sclerosis. Brain 2000; 123: 641– 649 . - PubMed
-
- Dyment DA, Cader MZ, Willer CJ, Risch N, Sadovnick AD, Ebers GC. A multigenerational family with multiple sclerosis. Brain 2002; 125: 1474– 1482 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
