Mapping quantitative trait loci onto a phylogenetic tree
- PMID: 22745229
- PMCID: PMC3430541
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.112.142448
Mapping quantitative trait loci onto a phylogenetic tree
Abstract
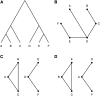
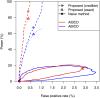
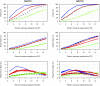
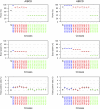
Despite advances in genetic mapping of quantitative traits and in phylogenetic comparative approaches, these two perspectives are rarely combined. The joint consideration of multiple crosses among related taxa (whether species or strains) not only allows more precise mapping of the genetic loci (called quantitative trait loci, QTL) that contribute to important quantitative traits, but also offers the opportunity to identify the origin of a QTL allele on the phylogenetic tree that relates the taxa. We describe a formal method for combining multiple crosses to infer the location of a QTL on a tree. We further discuss experimental design issues for such endeavors, such as how many crosses are required and which sets of crosses are best. Finally, we explore the method's performance in computer simulations, and we illustrate its use through application to a set of four mouse intercrosses among five inbred strains, with data on HDL cholesterol.
Figures

References
-
- Bradshaw H. D., Wilbert S. M., Otto K. G., Schemske D. W., 1995. Genetic mapping of floral traits associated with reproductive isolation in monkey flowers (Mimulus). Nature 376: 762–765
-
- Broman K. W., Wu H., Sen S., Churchill G. A., 2003. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19: 889–890 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

