Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone isoforms: parallel secretion of total and 20-kDa growth hormone and relation to insulin sensitivity in healthy humans
- PMID: 22745239
- PMCID: PMC3431574
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2012-2012
Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone isoforms: parallel secretion of total and 20-kDa growth hormone and relation to insulin sensitivity in healthy humans
Abstract
Context: The 20-kDa human GH (hGH) is produced in the pituitary by alternative splicing of the hGH-N gene. The 20-kDa hGH promotes growth similarly to 22-kDa or total hGH, the predominant form in circulation, but the relative effects of these isoforms on glucose metabolism have been debated.
Objective: To investigate the effect of ghrelin on 20-kDa and total hGH secretion in healthy, nonobese subjects. We also studied associations between basal GH concentration and fasting glucose and insulin as well as between dynamic GH secretion and insulin sensitivity.
Design and setting: Synthetic human acyl ghrelin (0.2 or 0.6 nmol/kg · h) or saline was infused in random order in 14 healthy subjects (six males, eight females; age 27.7 ± 6.3 yr; body mass index 22.0 ± 2.7 kg/m(2), mean ± SEM) on 3 separate days. Ghrelin was infused for 45 min to achieve steady-state levels and continued through a 3-h frequently sampled i.v. glucose tolerance test. Insulin sensitivity index was quantified using the minimal model of glucose kinetics.
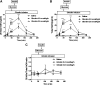
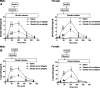
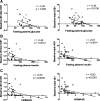
Results: Basal 20-kDa and total GH concentrations were 0.4 ± 0.1 and 2.2 ± 0.4 ng/ml, respectively, with a 20-kDa to total GH ratio of 0.13 ± 0.02. Females had significantly higher baseline GH levels. Ghrelin administration increased 20-kDa and total GH levels in a parallel and dose-dependent fashion, with no significant change in the ratio of the isoforms. Basal 20-kDa and total GH levels were negatively correlated with fasting glucose, insulin, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance. During the frequently sampled iv glucose tolerance test, GH secretion was positively correlated with insulin sensitivity index with saline infusion.
Conclusion: Ghrelin dose-dependently increases endogenous 20-kDa and total GH secretion in a parallel fashion in healthy subjects. Both basal and stimulated levels of the different GH isoforms were positively associated with insulin sensitivity in this cohort of healthy men and women.
Figures
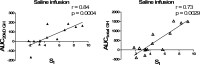
References
-
- Baumann G. 1991. Growth hormone heterogeneity: genes, isohormones, variants, and binding proteins. Endocr Rev 12:424–449 - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa M, Yokoya S, Tachibana K, Hasegawa Y, Yasuda T, Tokuhiro E, Hashimoto Y, Tanaka T. 1999. Serum levels of 20-kilodalton human growth hormone (GH) are parallel those of 22-kilodalton human GH in normal and short children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:98–104 - PubMed
-
- Wallis M. 1980. Growth hormone: deletions in the protein and introns in the gene. Nature 284:512. - PubMed
-
- Wada M, Uchida H, Ikeda M, Tsunekawa B, Naito N, Banba S, Tanaka E, Hashimoto Y, Honjo M. 1998. The 20-kilodalton (kDa) human growth hormone (hGH) differs from the 22-kDa hGH in the complex formation with cell surface hGH receptor and hGH-binding protein circulating in human plasma. Mol Endocrinol 12:146–156 - PubMed
-
- Lewis UJ, Dunn JT, Bonewald LF, Seavey BK, Vanderlaan WP. 1978. A naturally occurring structural variant of human growth hormone. J Biol Chem 253:2679–2687 - PubMed

