A genome-wide transgenic resource for conditional expression of Drosophila microRNAs
- PMID: 22745315
- PMCID: PMC3392707
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.079939
A genome-wide transgenic resource for conditional expression of Drosophila microRNAs
Abstract
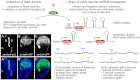
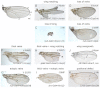
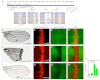
microRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous short RNAs that mediate vast networks of post-transcriptional gene regulation. Although computational searches and experimental profiling provide evidence for hundreds of functional targets for individual miRNAs, such data rarely provide clear insight into the phenotypic consequences of manipulating miRNAs in vivo. We describe a genome-wide collection of 165 Drosophila miRNA transgenes and find that a majority induced specific developmental defects, including phenocopies of mutants in myriad cell-signaling and patterning genes. Such connections allowed us to validate several likely targets for miRNA-induced phenotypes. Importantly, few of these phenotypes could be predicted from computationally predicted target lists, thus highlighting the value of whole-animal readouts of miRNA activities. Finally, we provide an example of the relevance of these data to miRNA loss-of-function conditions. Whereas misexpression of several K box miRNAs inhibited Notch pathway activity, reciprocal genetic interaction tests with miRNA sponges demonstrated endogenous roles of the K box miRNA family in restricting Notch signaling. In summary, we provide extensive evidence that misexpression of individual miRNAs often induces specific mutant phenotypes that can guide their functional study. By extension, these data suggest that the deregulation of individual miRNAs in other animals may frequently yield relatively specific phenotypes during disease conditions.
Figures



References
-
- Aravin A., Lagos-Quintana M., Yalcin A., Zavolan M., Marks D., Snyder B., Gaasterland T., Meyer J., Tuschl T. (2003). The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev. Cell 5, 337-350 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

