Regulation of neuronal proapoptotic potassium currents by the hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A
- PMID: 22745487
- PMCID: PMC3388847
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0937-12.2012
Regulation of neuronal proapoptotic potassium currents by the hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A
Abstract
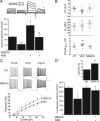
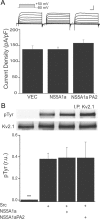
Apoptosis-enabling neuronal potassium efflux is mediated by an enhancement of K+ currents. In cortical neurons, increased currents are triggered by dual phosphorylation of Kv2.1 by Src and p38 at channel residues Y124 and S800. It was recently shown that a K+ current surge is also present in hepatocytes undergoing apoptosis, and that the hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) could inhibit Kv2.1-mediated currents and block cell death. Here, we show that NS5A1b (from HCV genotype 1b) expression in rat neurons depresses delayed rectifier potassium currents, limits the magnitude of the K+ current surge following exposure to activated microglia, and is neuroprotective. In a non-neuronal recombinant expression system, cells expressing Kv2.1 mutated at residue Y124, but not S800 mutants, are insensitive to NS5A1b-mediated current inhibition. Accordingly, NS5A1b coexpression prevents phosphorylation of wild-type Kv2.1 by Src at Y124, but is unable to inhibit p38 phosphorylation of the channel at S800. The actions of the viral protein are genotype-selective, as NS5A1a does not depress neuronal potassium currents nor inhibit Src phosphorylation of Kv2.1. Our results indicate that NS5A1b limits K+ currents following injury, leading to increased neuronal viability. NS5A1b may thus serve as a model for a new generation of neuroprotective agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Critical role of Casein kinase 2 in hepatitis C NS5A-mediated inhibition of Kv2.1 K(+) channel function.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Nov 16;609:48-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.021. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 26472706 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic surge of potassium currents is mediated by p38 phosphorylation of Kv2.1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 27;104(9):3568-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610159104. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360683 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Pro-Apoptotic Phosphorylation of Kv2.1 K+ Channels.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 26;10(6):e0129498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129498. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26115091 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of KV2.1 somato-dendritic clusters prevents the apoptogenic increase of potassium currents.Neuroscience. 2017 Jun 23;354:158-167. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.04.034. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28461216 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of the voltage-gated Kv2.1 potassium channel by multisite phosphorylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):1064-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0351064. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956280 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C virus and hepatocellular carcinoma.Biology (Basel). 2013 Jan 30;2(1):304-16. doi: 10.3390/biology2010304. Biology (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24832662 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin type 4 receptor-mediated inhibition of A-type K+ current enhances sensory neuronal excitability and mechanical pain sensitivity in rats.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 5;294(14):5496-5507. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006894. Epub 2019 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30745360 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels as Regulators of Cell Death.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 14;8:611853. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.611853. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33381507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibits mixed lineage kinase 3 to block apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24753-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491985. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23857585 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Neuroprotection Induced by Zinc-Dependent Expression of Hepatitis C-Derived Protein NS5A Targeting Kv2.1 Potassium Channels.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Nov;367(2):348-355. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.252338. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018. PMID: 30190339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aras MA, Hartnett KA, Aizenman E. Assessment of cell viability in primary neuronal cultures. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter. 2008;7 Unit 7.18. - PubMed
-
- Cheepsunthorn P, Radov L, Menzies S, Reid J, Connor JR. Characterization of a novel brain-derived microglial cell line isolated from neonatal rat brain. Glia. 2001;35:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Dal Pero F, Di Maira G, Marin O, Bortoletto G, Pinna LA, Alberti A, Ruzzene M, Gerotto M. Heterogeneity of CK2 phosphorylation sites in the NS5A protein of different hepatitis C virus genotypes. J Hepatol. 2007;47:768–776. - PubMed
-
- Hartnett KA, Stout AK, Rajdev S, Rosenberg PA, Reynolds IJ, Aizenman E. NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity: a paradoxical requirement for extracellular Mg2+ in Na+/Ca2+-free solutions in rat cortical neurons in vitro. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1836–1845. - PubMed
-
- He Y, Staschke KA, Tan SL. HCV NS5A: a multifunctional regulator of cellular pathways and virus replication. In: Tan SL, editor. Hepatitis C viruses: genomes and molecular biology. Norfolk, UK: Horizon Bioscience; 2006. pp. 267–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
