MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant
- PMID: 22745489
- PMCID: PMC4434222
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0558-12.2012
MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant
Abstract
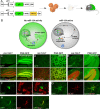
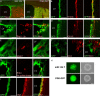
New neurons are continuously generated from neural stem cells with astrocyte properties, which reside in close proximity to the ventricle in the postnatal and adult brain. In this study we found that microRNA-124 (miR-124) dictates postnatal neurogenesis in the mouse subventricular zone. Using a transgenic reporter mouse we show that miR-124 expression is initiated in the rapid amplifying progenitors and remains expressed in the resulting neurons. When we stably inhibited miR-124 in vivo, neurogenesis was blocked, leading to the appearance of ectopic cells with astrocyte characteristics in the olfactory bulb. Conversely, when we overexpressed miR-124, neural stem cells were not maintained in the subventricular zone and neurogenesis was lost. In summary, our results demonstrate that miR-124 is a neuronal fate determinant in the subventricular zone.
Figures





References
-
- Ahlenius H, Kokaia Z. Isolation and generation of neurosphere cultures from embryonic and adult mouse brain. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;633:241–252. - PubMed
-
- Brown BD, Gentner B, Cantore A, Colleoni S, Amendola M, Zingale A, Baccarini A, Lazzari G, Galli C, Naldini L. Endogenous microRNA can be broadly exploited to regulate transgene expression according to tissue, lineage and differentiation state. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1457–1467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
