Thrombospondin-4 contributes to spinal sensitization and neuropathic pain states
- PMID: 22745497
- PMCID: PMC3408211
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6494-11.2012
Thrombospondin-4 contributes to spinal sensitization and neuropathic pain states
Abstract
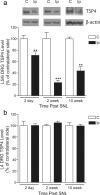
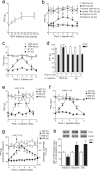
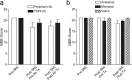
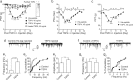
Neuropathic pain is a common cause of pain after nerve injury, but its molecular basis is poorly understood. In a post-gene chip microarray effort to identify new target genes contributing to neuropathic pain development, we report here the characterization of a novel neuropathic pain contributor, thrombospondin-4 (TSP4), using a neuropathic pain model of spinal nerve ligation injury. TSP4 is mainly expressed in astrocytes and significantly upregulated in the injury side of dorsal spinal cord that correlates with the development of neuropathic pain states. TSP4 blockade by intrathecal antibodies, antisense oligodeoxynucleotides, or inactivation of the TSP4 gene reverses or prevents behavioral hypersensitivities. Intrathecal injection of TSP4 protein into naive rats is sufficient to enhance the frequency of EPSCs in spinal dorsal horn neurons, suggesting an increased excitatory presynaptic input, and to cause similar behavioral hypersensitivities. Together, these findings support that injury-induced spinal TSP4 may contribute to spinal presynaptic hypersensitivity and neuropathic pain states. Development of TSP4 antagonists has the therapeutic potential for target-specific neuropathic pain management.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Trigeminal nerve injury-induced thrombospondin-4 up-regulation contributes to orofacial neuropathic pain states in a rat model.Eur J Pain. 2014 Apr;18(4):489-95. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00396.x. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Eur J Pain. 2014. PMID: 24019258 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium channel alpha-2-delta-1 protein upregulation in dorsal spinal cord mediates spinal cord injury-induced neuropathic pain states.Pain. 2011 Mar;152(3):649-655. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.12.014. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Pain. 2011. PMID: 21239111 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-4 contributes to spinal cord injury-induced changes in nociception.Eur J Pain. 2013 Nov;17(10):1458-64. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00326.x. Epub 2013 May 7. Eur J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23649982 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Analgesia by Gabapentinoid Drugs: Involvement of Modulation of Synaptogenesis and Trafficking of Glutamate-Gated Ion Channels.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Jan 2;388(1):121-133. doi: 10.1124/jpet.123.001669. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 37918854 Review.
-
The Role of the Spinal Wnt Signaling Pathway in HIV-Related Neuropathic Pain.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Oct;40(7):1075-1085. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00805-6. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32100186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocyte-derived thrombospondins mediate the development of hippocampal presynaptic plasticity in vitro.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13100-10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2604-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993427 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cyanocobalamin and its combination with morphine on neuropathic rats and the relationship between these effects and thrombospondin-4 expression.Korean J Pain. 2022 Jan 1;35(1):66-77. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.1.66. Korean J Pain. 2022. PMID: 34966013 Free PMC article.
-
Painful nerve injury upregulates thrombospondin-4 expression in dorsal root ganglia.J Neurosci Res. 2015 Mar;93(3):443-53. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23498. Epub 2014 Oct 18. J Neurosci Res. 2015. PMID: 25327416 Free PMC article.
-
Toward discovering a novel family of peptides targeting neuroinflammatory states of brain microglia and astrocytes.J Neurochem. 2024 Oct;168(10):3386-3414. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15840. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Neurochem. 2024. PMID: 37171455
-
Injury-induced maladaptation and dysregulation of calcium channel α2 δ subunit proteins and its contribution to neuropathic pain development.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;175(12):2231-2243. doi: 10.1111/bph.13930. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28646556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams JC. Thrombospondins: multifunctional regulators of cell interactions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:25–51. - PubMed
-
- Barlow AL, Macleod A, Noppen S, Sanderson J, Guérin CJ. Colocalization analysis in fluorescence micrographs: verification of a more accurate calculation of Pearson's correlation coefficient. Microsc Microanal. 2010;16:710–724. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
