Differential role of gp130-dependent STAT and Ras signalling for haematopoiesis following bone-marrow transplantation
- PMID: 22745821
- PMCID: PMC3382143
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039728
Differential role of gp130-dependent STAT and Ras signalling for haematopoiesis following bone-marrow transplantation
Abstract
Introduction: Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is a complex process regulated by different cytokines and growth factors. The pleiotropic cytokine IL-6 (Interleukin-6) and related cytokines of the same family acting on the common signal transducer gp130 are known to play a key role in bone marrow (BM) engraftment. In contrast, the exact signalling events that control IL-6/gp130-driven haematopoietic stem cell development during BMT remain unresolved.
Methods: Conditional gp130 knockout and knockin mice were used to delete gp130 expression (gp130(ΔMx)), or to selectively disrupt gp130-dependent Ras (gp130(ΔMxRas)) or STAT signalling (gp130(ΔMxSTAT)) in BM cells. BM derived from the respective strains was transplanted into irradiated wildtype hosts and repopulation of various haematopoietic lineages was monitored by flow cytometry.
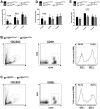
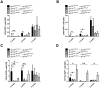
Results: BM derived from gp130 deficient donor mice (gp130(ΔMx)) displayed a delayed engraftment, as evidenced by reduced total white blood cells (WBC), marked thrombocytopenia and anaemia in the early phase after BMT. Lineage analysis unravelled a restricted development of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cells, CD19(+) B-cells and CD11b(+) myeloid cells after transplantation of gp130-deficient BM grafts. To further delineate the two major gp130-induced signalling cascades, Ras-MAPK and STAT1/3-signalling respectively, we used gp130(ΔMxRas) and gp130(ΔMxSTAT) donor BM. BMT of gp130(ΔMxSTAT) cells significantly impaired engraftment of CD4(+), CD8(+), CD19(+) and CD11b(+) cells, whereas gp130(ΔMxRas) BM displayed a selective impairment in early thrombopoiesis. Importantly, gp130-STAT1/3 signalling deficiency in BM grafts severely impaired survival of transplanted mice, thus demonstrating a pivotal role for this pathway in BM graft survival and function.
Conclusion: Our data unravel a vital function of IL-6/gp130-STAT1/3 signals for BM engraftment and haematopoiesis, as well as for host survival after transplantation. STAT1/3 and ras-dependent pathways thereby exert distinct functions on individual bone-marrow-lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hematopoietic abnormalities in mice deficient in gp130-mediated STAT signaling.Exp Hematol. 2002 Nov;30(11):1248-56. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(02)00929-3. Exp Hematol. 2002. PMID: 12423677
-
Murine Oncostatin M Acts via Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor to Phosphorylate Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) but Not STAT1, an Effect That Protects Bone Mass.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 7;291(41):21703-21716. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.748483. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27539849 Free PMC article.
-
Ciliary neurotrophic factor has intrinsic and extrinsic roles in regulating B cell differentiation and bone structure.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 21;5:15529. doi: 10.1038/srep15529. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26487326 Free PMC article.
-
Ups and downs: the STAT1:STAT3 seesaw of Interferon and gp130 receptor signalling.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008 Aug;19(4):351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Jun 22. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18620071 Review.
-
Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: the gp130-STAT axis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2007 Sep;102(5):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0674-z. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17918316 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory effect of anti-gp130 functional mAb on IL-6 mediated RANKL and Wnt5a expression through JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway in FLS.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 4;9(29):20366-20376. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23917. eCollection 2018 Apr 17. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29755657 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

