Relationship between Respiratory Load Perception and Perception of Nonrespiratory Sensory Modalities in Subjects with Life-Threatening Asthma
- PMID: 22745905
- PMCID: PMC3382357
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/310672
Relationship between Respiratory Load Perception and Perception of Nonrespiratory Sensory Modalities in Subjects with Life-Threatening Asthma
Abstract
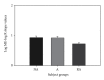
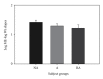
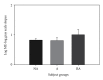
Subjects with life-threatening asthma (LTA) have reported decreased sensitivity to inspiratory resistive (R) loads. It is unknown if decreased sensitivity is specific for inspiratory R loads, other types of respiratory loads, or a general deficit affecting sensory modalities. This study hypothesized that impairment is specific to respiratory stimuli. This study tested perceptual sensitivity of LTA, asthmatic (A), and nonasthmatic (NA) subjects to 4 sensory modalities: respiratory, somatosensory, auditory, visual. Perceptual sensitivity was measured with magnitude estimation (ME): respiratory loads ME, determined using inspiratory R and pressure threshold (PT) loads; somatosensory ME, determined using weight ranges of 2-20 kg; auditory ME, determined using graded magnitudes of 1 kHz tones delivered for 3 seconds bilaterally; visual ME, determined using gray-to-white disk intensity gradations on black background. ME for inspiratory R loads lessened for LTA over A and NA subjects. There was no significant difference between the 3 groups in ME for PT inspiratory loads, weight, sound, and visual trials. These results demonstrate that LTA subjects are poor perceivers of inspiratory R loads. This deficit in respiratory perception is specific to inspiratory R loads and is not due to perceptual deficits in other types of inspiratory loads, somatosensory, auditory, or visual sensory modalities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Magnitude estimation of inspiratory resistive loads in children with life-threatening asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Nov;156(5):1530-5. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.156.5.9703011. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. PMID: 9372671
-
Perception of multiple-breath inspiratory resistive loads in males and females.Biol Psychol. 2010 Apr;84(1):147-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.03.004. Epub 2010 Mar 21. Biol Psychol. 2010. PMID: 20227459 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory-related evoked potentials in children with life-threatening asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Jun;161(6):1830-5. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.6.9903077. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 10852753
-
Inspiratory resistive load detection in children with life-threatening asthma.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001 Jul;32(1):44-8. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1087. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001. PMID: 11416875
-
Effect of acute intermittent hypoxia treatment on ventilatory load compensation and magnitude estimation of inspiratory resistive loads in an individual with chronic incomplete cervical spinal cord injury.J Spinal Cord Med. 2016;39(1):103-10. doi: 10.1179/2045772314Y.0000000277. Epub 2014 Nov 15. J Spinal Cord Med. 2016. PMID: 25400130 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ventilatory control in infants, children, and adults with bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013 Nov 1;189(2):329-37. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23886637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Sensory Monitoring on Speech Breathing Planning Processes: An Exploratory Study in Aging Speakers Reporting Dyspnea.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2024 Aug 5;67(8):2483-2498. doi: 10.1044/2024_JSLHR-23-00673. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2024. PMID: 38980884 Free PMC article.
-
Being Anxious, Thinking Positively: The Effect of Emotional Context on Respiratory Sensory Gating.Front Physiol. 2016 Feb 16;7:19. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00019. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26909040 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory modulation of startle eye blink: a new approach to assess afferent signals from the respiratory system.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Nov 19;371(1708):20160019. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0019. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 28080976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davenport PW, Cruz M, Stecenko AA, Kifle Y. Respiratory-related evoked potentials in children with life-threatening asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2000;161(6):1830–1835. - PubMed
-
- Kifle Y, Seng V, Davenport PW. Magnitude estimation of inspiratory resistive loads in children with life-threatening asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 1997;156(5):1530–1535. - PubMed
-
- Kikuchi Y, Hida W, Chonan T, Shindoh C, Sasaki H, Takishima T. Decrease in functional residual capacity during inspiratory loading and the sensation of dyspnea. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1991;71(5):1787–1794. - PubMed
-
- Julius SM, Davenport KL, Davenport PW. Perception of intrinsic and extrinsic respiratory loads in children with life-threatening asthma. Pediatric Pulmonology. 2002;34(6):425–433. - PubMed
-
- Sherman JM, Capen CL. The red alert program for life-threatening asthma. Pediatrics. 1997;100(2):187–191. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

