Mouse skeletal muscle fiber-type-specific macroautophagy and muscle wasting are regulated by a Fyn/STAT3/Vps34 signaling pathway
- PMID: 22745922
- PMCID: PMC3383827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.03.014
Mouse skeletal muscle fiber-type-specific macroautophagy and muscle wasting are regulated by a Fyn/STAT3/Vps34 signaling pathway
Abstract
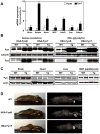
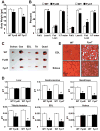
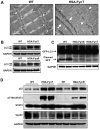
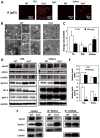
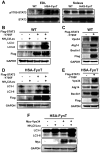
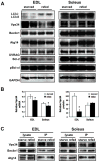
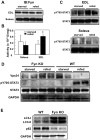
Skeletal muscle atrophy induced by aging (sarcopenia), inactivity, and prolonged fasting states (starvation) is predominantly restricted to glycolytic type II muscle fibers and typical spares oxidative type I fibers. However, the mechanisms accounting for muscle fiber-type specificity of atrophy have remained enigmatic. In the current study, although the Fyn tyrosine kinase activated the mTORC1 signaling complex, it also induced marked atrophy of glycolytic fibers with relatively less effect on oxidative muscle fibers. This was due to inhibition of macroautophagy via an mTORC1-independent but STAT3-dependent reduction in Vps34 protein levels and decreased Vps34/p150/Beclin1/Atg14 complex 1. Physiologically, in the fed state endogenous Fyn kinase activity was increased in glycolytic but not oxidative skeletal muscle. In parallel, Y705-STAT3 phosphorylation increased with decreased Vps34 protein levels. Moreover, fed/starved regulation of Y705-STAT3 phosphorylation and Vps34 protein levels was prevented in skeletal muscle of Fyn null mice. These data demonstrate a Fyn/STAT3/Vps34 pathway that is responsible for fiber-type-specific regulation of macroautophagy and skeletal muscle atrophy.
Keywords: Fyn; LKB1; STAT3; Vps34; autophagy; mTORC1; muscle atrophy.
Copyright © 2012 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fyn Activation of mTORC1 Stimulates the IRE1α-JNK Pathway, Leading to Cell Death.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 9;290(41):24772-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.687020. Epub 2015 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26306048 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-carbohydrate ingestion alters Vps34 cellular localization independent of changes in kinase activity in human skeletal muscle.Exp Physiol. 2020 Dec;105(12):2178-2189. doi: 10.1113/EP088805. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Exp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32965751
-
AMPK promotes skeletal muscle autophagy through activation of forkhead FoxO3a and interaction with Ulk1.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Feb;113(2):695-710. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23399. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22006269
-
Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling.Cell Res. 2014 Jan;24(1):42-57. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.166. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24343578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of protein synthesis by amino acids in muscle of neonates.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(4):1445-60. doi: 10.2741/3798. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy is required for exercise training-induced skeletal muscle adaptation and improvement of physical performance.FASEB J. 2013 Oct;27(10):4184-93. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-228486. Epub 2013 Jun 27. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23825228 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative muscles have better mitochondrial homeostasis than glycolytic muscles throughout life and maintain mitochondrial function during aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Nov 18;10(11):3327-3352. doi: 10.18632/aging.101643. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 30449736 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn kinase regulates dopaminergic neuronal apoptosis in animal and cell models of high glucose (HG) treatment.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Dec 4;22(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12860-021-00398-y. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34863087 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Fyn and the interleukin-6-STAT-3-autophagy axis in sarcopenia.iScience. 2023 Aug 25;26(10):107717. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107717. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37744036 Free PMC article.
-
4-Octyl itaconate attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2 and inhibiting STAT3 signaling.Mol Med. 2023 Apr 24;29(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00631-8. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37095432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:137–163. - PubMed
-
- Backer JM. The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J. 2008;410:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Signaling pathways in skeletal muscle remodeling. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:19–37. - PubMed
-
- Bastie C, Zong H, Xu J, Busa B, Judex S, Kurland IJ, Pessin JE. Role of the Src Kinase Family Member Fyn in the Integrative Metabolic Regulation of Peripheral Tissue Fatty Acid Oxidation. Cell Metab. 2007;5 - PubMed
-
- Bechet D, Tassa A, Taillandier D, Combaret L, Attaix D. Lysosomal proteolysis in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:2098–2114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

