Redox-sensitive oxidation and phosphorylation of PTEN contribute to enhanced activation of PI3K/Akt signaling in rostral ventrolateral medulla and neurogenic hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 22746319
- PMCID: PMC3503464
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2011.4457
Redox-sensitive oxidation and phosphorylation of PTEN contribute to enhanced activation of PI3K/Akt signaling in rostral ventrolateral medulla and neurogenic hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
Aims: The activity of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/serine/threonine protein kinase (Akt) is enhanced under hypertension. The phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) is a negative regulator of PI3K signaling, and its activity is redox-sensitive. In the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), which is responsible for the maintenance of blood pressure, oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in neurogenic hypertension. The present study evaluated the hypothesis that redox-sensitive inactivation of PTEN results in enhanced PI3K/Akt signaling in RVLM, leading to neurogenic hypertension.
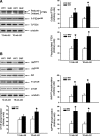
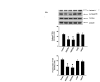
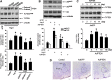
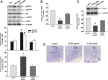
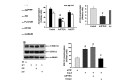
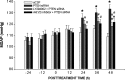
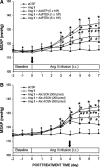
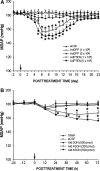
Results: Compared to age-matched normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats, PTEN inactivation in the form of oxidation and phosphorylation were greater in RVLM of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). PTEN inactivation was accompanied by augmented PI3K activity and PI3K/Akt signaling, as reflected by the increase in phosphorylation of Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin. Intracisternal infusion of tempol or microinjection into the bilateral RVLM of adenovirus encoding superoxide dismutase significantly antagonized the PTEN inactivation and blunted the enhanced PI3K/Akt signaling in SHR. Gene transfer of PTEN to RVLM in SHR also abrogated the enhanced Akt activation and promoted antihypertension. Silencing PTEN expression in RVLM with small-interfering RNA, on the other hand, augmented PI3K/Akt signaling and promoted long-term pressor response in normotensive WKY rats.
Innovation: The present study demonstrated for the first time that the redox-sensitive check-and-balance process between PTEN and PI3K/Akt signaling is engaged in the pathogenesis of hypertension.
Conclusion: We conclude that an aberrant interplay between the redox-sensitive PTEN and PI3k/Akt signaling in RVLM underpins neural mechanism of hypertension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K/Akt signaling, sustains brain stem cardiovascular regulation during mevinphos intoxication.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:175-185. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28601397
-
Redox-sensitive endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy at rostral ventrolateral medulla contribute to hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Hypertension. 2013 Jun;61(6):1270-80. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00469. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23608659
-
Centrally acting drug moxonidine decreases reactive oxygen species via inactivation of the phosphoinositide-3 kinase signaling in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 2016 May;34(5):993-1004. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000887. J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26886567
-
PTEN/FLJ10540/PI3K/Akt cascade in experimental brain stem death: A newfound role for a classical tumorigenic signaling pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;155:207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30008438 Review.
-
PI3K/AKT Pathway and Its Mediators in Thyroid Carcinomas.Mol Diagn Ther. 2016 Feb;20(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0175-y. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26597586 Review.
Cited by
-
The phosphoinositide-3 kinase signaling is involved in neuroinflammation in hypertensive rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017 Apr;23(4):350-359. doi: 10.1111/cns.12679. Epub 2017 Feb 12. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017. PMID: 28191736 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Increases Sestrin 2 Content by Reducing Its Degradation through the PI 3 K/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:505849. doi: 10.1155/2015/505849. Epub 2015 Feb 22. Int J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25792980 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing Advances the Genetic Diagnosis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM).Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;11(7):1294. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071294. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883785 Free PMC article.
-
Methylmercury, an environmental electrophile capable of activation and disruption of the Akt/CREB/Bcl-2 signal transduction pathway in SH-SY5Y cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 30;6:28944. doi: 10.1038/srep28944. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27357941 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Energy Metabolism and Disturbed Dopamine and Glutamate Signalling in the Striatum and Prefrontal Cortex of the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Jul;56(3):696-707. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0491-z. Epub 2015 Feb 11. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25665550
References
-
- Blanco-Aparicio C. Renner O. Leal JF. Carnero A. PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:1379–1386. - PubMed
-
- Chan JYH. Wang LL. Chao YM. Chan SHH. Downregulation of basal iNOS at the rostral ventrolateral medulla is innate in SHR. Hypertension. 2003;41:563–570. - PubMed
-
- Chan SHH. Hsu KS. Huang CC. Wang LL. Ou CC. Chan JYH. NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide anion mediates angiotensin II-induced pressor effect via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Circ Res. 2005;97:772–780. - PubMed
-
- Chan SHH. Tai MH. Li CY. Chan JYH. Reduction in molecular synthesis or enzyme activity of superoxide dismutases and catalase contributes to oxidative stress and neurogenic hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:2028–2039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

