Single-base resolution maps of cultivated and wild rice methylomes and regulatory roles of DNA methylation in plant gene expression
- PMID: 22747568
- PMCID: PMC3447678
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-300
Single-base resolution maps of cultivated and wild rice methylomes and regulatory roles of DNA methylation in plant gene expression
Abstract
Background: DNA methylation plays important biological roles in plants and animals. To examine the rice genomic methylation landscape and assess its functional significance, we generated single-base resolution DNA methylome maps for Asian cultivated rice Oryza sativa ssp. japonica, indica and their wild relatives, Oryza rufipogon and Oryza nivara.
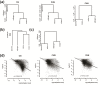
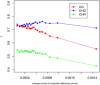
Results: The overall methylation level of rice genomes is four times higher than that of Arabidopsis. Consistent with the results reported for Arabidopsis, methylation in promoters represses gene expression while gene-body methylation generally appears to be positively associated with gene expression. Interestingly, we discovered that methylation in gene transcriptional termination regions (TTRs) can significantly repress gene expression, and the effect is even stronger than that of promoter methylation. Through integrated analysis of genomic, DNA methylomic and transcriptomic differences between cultivated and wild rice, we found that primary DNA sequence divergence is the major determinant of methylational differences at the whole genome level, but DNA methylational difference alone can only account for limited gene expression variation between the cultivated and wild rice. Furthermore, we identified a number of genes with significant difference in methylation level between the wild and cultivated rice.
Conclusions: The single-base resolution methylomes of rice obtained in this study have not only broadened our understanding of the mechanism and function of DNA methylation in plant genomes, but also provided valuable data for future studies of rice epigenetics and the epigenetic differentiation between wild and cultivated rice.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

