A novel autoantibody against fibronectin leucine-rich transmembrane protein 2 expressed on the endothelial cell surface identified by retroviral vector system in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22747982
- PMCID: PMC3580549
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3897
A novel autoantibody against fibronectin leucine-rich transmembrane protein 2 expressed on the endothelial cell surface identified by retroviral vector system in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: Anti-endothelial cell antibodies (AECAs) are thought to be critical for vasculitides in collagen diseases, but most were directed against molecules localized within the cell and not expressed on the cell surface. To clarify the pathogenic roles of AECAs, we constructed a retroviral vector system for identification of autoantigens expressed on the endothelial cell surface.
Methods: AECA activity in sera from patients with collagen diseases was measured with flow cytometry by using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). A cDNA library of HUVECs was retrovirally transfected into a rat myeloma cell line, from which AECA-positive clones were sorted with flow cytometry. cDNA of the cells was analyzed to identify an autoantigen, and then the clinical characteristics and the functional significance of the autoantibody were evaluated.
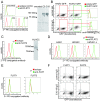
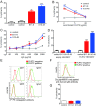
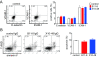
Results: Two distinct AECA-positive clones were isolated by using serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) from a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Both clones were identical to cDNA of fibronectin leucine-rich transmembrane protein 2 (FLRT2). HUVECs expressed FLRT2 and the prototype AECA IgG bound specifically to FLRT2-transfected cells. Anti-FLRT2 antibody activity accounted for 21.4% of AECAs in SLE. Furthermore, anti-FLRT2 antibody induced complement-dependent cytotoxicity against FLRT2-expressing cells.
Conclusions: We identified the membrane protein FLRT2 as a novel autoantigen of AECAs in SLE patients by using the retroviral vector system. Anti-FLRT2 antibody has the potential to induce direct endothelial cell cytotoxicity in about 10% of SLE patients and could be a novel molecular target for intervention. Identification of such a cell-surface target for AECAs may reveal a comprehensive mechanism of vascular injury in collagen diseases.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An innovative method to identify autoantigens expressed on the endothelial cell surface: serological identification system for autoantigens using a retroviral vector and flow cytometry (SARF).Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:453058. doi: 10.1155/2013/453058. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23401699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of endothelial cell apoptosis by heat-shock protein 60-reactive antibodies from anti-endothelial cell autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus patients.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Oct;50(10):3221-31. doi: 10.1002/art.20564. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15476243
-
Identification of candidate endothelial cell autoantigens in systemic lupus erythematosus using a molecular cloning strategy: a role for ribosomal P protein P0 as an endothelial cell autoantigen.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000 Oct;39(10):1114-20. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.10.1114. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000. PMID: 11035132
-
The impact of anti-endothelial cell antibodies (AECAs) on the development of blood vessel damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: the preliminary study.Rheumatol Int. 2022 May;42(5):791-801. doi: 10.1007/s00296-022-05104-5. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Rheumatol Int. 2022. PMID: 35284968
-
Antiendothelial cell antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus.Autoimmun Rev. 2002 Dec;1(6):365-72. doi: 10.1016/s1568-9972(02)00063-0. Autoimmun Rev. 2002. PMID: 12848993 Review.
Cited by
-
An innovative method to identify autoantigens expressed on the endothelial cell surface: serological identification system for autoantigens using a retroviral vector and flow cytometry (SARF).Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:453058. doi: 10.1155/2013/453058. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23401699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active withdrawal of corticosteroids using tocilizumab and its association with autoantibody profiles in relapsed Takayasu arteritis: a multicentre, single-arm, prospective study (the Ab-TAK study).Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1473100. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1473100. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840060 Free PMC article.
-
A Glimpse into Humoral Response and Related Therapeutic Approaches of Takayasu's Arteritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 13;25(12):6528. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126528. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common Autoantibody among Takayasu Arteritis and Ulcerative Colitis: A Possible Pathophysiology That Includes Gut-Vessel Connection in Vascular Inflammation.JMA J. 2023 Jul 14;6(3):265-273. doi: 10.31662/jmaj.2023-0038. Epub 2023 May 29. JMA J. 2023. PMID: 37560375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Signaling Pathways in Medium and Large Vessel Vasculitis.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:587089. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.587089. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

