A systematic comparison and evaluation of high density exon arrays and RNA-seq technology used to unravel the peripheral blood transcriptome of sickle cell disease
- PMID: 22747986
- PMCID: PMC3428653
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-28
A systematic comparison and evaluation of high density exon arrays and RNA-seq technology used to unravel the peripheral blood transcriptome of sickle cell disease
Abstract
Background: Transcriptomic studies in clinical research are essential tools for deciphering the functional elements of the genome and unraveling underlying disease mechanisms. Various technologies have been developed to deduce and quantify the transcriptome including hybridization and sequencing-based approaches. Recently, high density exon microarrays have been successfully employed for detecting differentially expressed genes and alternative splicing events for biomarker discovery and disease diagnostics. The field of transcriptomics is currently being revolutionized by high throughput DNA sequencing methodologies to map, characterize, and quantify the transcriptome.
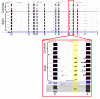
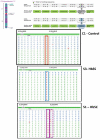
Methods: In an effort to understand the merits and limitations of each of these tools, we undertook a study of the transcriptome in sickle cell disease, a monogenic disease comparing the Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST microarray (Exon array) and Illumina's deep sequencing technology (RNA-seq) on whole blood clinical specimens.
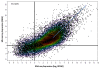
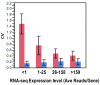
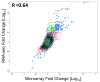
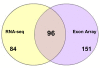
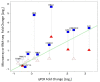
Results: Analysis indicated a strong concordance (R = 0.64) between Exon array and RNA-seq data at both gene level and exon level transcript expression. The magnitude of differential expression was found to be generally higher in RNA-seq than in the Exon microarrays. We also demonstrate for the first time the ability of RNA-seq technology to discover novel transcript variants and differential expression in previously unannotated genomic regions in sickle cell disease. In addition to detecting expression level changes, RNA-seq technology was also able to identify sequence variation in the expressed transcripts.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that microarrays remain useful and accurate for transcriptomic analysis of clinical samples with low input requirements, while RNA-seq technology complements and extends microarray measurements for novel discoveries.
Figures


References
-
- Rudan I. New technologies provide insights into genetic basis of psychiatric disorders and explain their co-morbidity. Psychiatr Danub. 2010;22(2):190–192. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Jiao R, Yang L, Wu LP, Li YR, Wang J. New-generation high-throughput technologies based 'omics' research strategy in human disease. Yi Chuan. 2011;33(8):829–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

