Paediatricians' perspectives on global health priorities for newborn care in a developing country: a national survey from Nigeria
- PMID: 22748076
- PMCID: PMC3519520
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-698X-12-9
Paediatricians' perspectives on global health priorities for newborn care in a developing country: a national survey from Nigeria
Abstract
Background: An understanding of the perception of paediatricians as key stakeholders in child healthcare delivery and the degree of congruence with current investment priorities is crucial in accelerating progress towards the attainment of global targets for child survival and overall health in developing countries. This study therefore elicited the views of paediatricians on current global priorities for newborn health in Nigeria as possible guide for policy makers.
Methods: Paediatric consultants and residents in the country were surveyed nationally between February and March 2011 using a questionnaire requiring the ranking of nine prominent and other neonatal conditions based separately on hospital admissions, mortality, morbidity and disability as well as based on all health indices in order of importance or disease burden. Responses were analysed with Friedman test and differences between subgroups of respondents with Mann-Whitney U test.
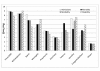
Results: Valid responses were received from 152 (65.8%) of 231 eligible physicians. Preterm birth/low birthweight ranked highest by all measures except for birth asphyxia which ranked highest for disability. Neonatal jaundice ranked next to sepsis by all measures except for disability and above tetanus except mortality. Preterm birth/low birthweight, birth asphyxia, sepsis, jaundice and meningitis ranked highest by composite measures while jaundice had comparable rating with sepsis. Birth trauma was most frequently cited under other unspecified conditions. There were no significant differences in ranking between consultants and residents except for birth asphyxia in relation to hospital admissions and morbidity as well as sepsis and tetanus in relation to mortality.
Conclusions: Current global priorities for neonatal survival in Nigeria largely accord with paediatricians' views except for neonatal jaundice which is commonly subsumed under "other" or "miscellaneous" neonatal conditions. While the importance of these priority conditions extends beyond mortality thus suggesting the need for a broader conceptualisation of newborn health to reflect the current realities, paediatricians should be actively engaged in advancing the attainment of global priorities for child survival and health in this population.
Figures
References
-
- Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Bassani DG, Jha P, Campbell H, Walker CF, Cibulskis R, Eisele T, Liu L, Mathers C. Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group of WHO and UNICEF. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:1969–1987. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60549-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lozano R, Wang H, Foreman KJ, Rajaratnam JK, Naghavi M, Marcus JR, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Lofgren KT, Phillips D, Atkinson C, Lopez AD, Murray CJ. Progress towards Millennium Development Goals 4 and 5 on maternal and child mortality: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet. 2011;378:1139–1165. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61337-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Commission on Social Determinants of Health (CSDH) Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through action on the social determinants of health. Final Report of the Commission on Social Determinants of Health. World Health Organization, Geneva; 2008.
-
- The Young Infants Clinical Signs Study Group. Clinical signs that predict severe illness in children under age 2 months: a multicentre study. Lancet. 2008;371:135–142. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources