Genetic correction of Huntington's disease phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 22748967
- PMCID: PMC3608272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.026
Genetic correction of Huntington's disease phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
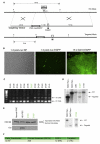
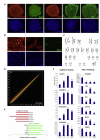
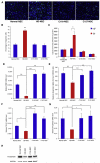
Huntington's disease (HD) is caused by a CAG expansion in the huntingtin gene. Expansion of the polyglutamine tract in the huntingtin protein results in massive cell death in the striatum of HD patients. We report that human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from HD patient fibroblasts can be corrected by the replacement of the expanded CAG repeat with a normal repeat using homologous recombination, and that the correction persists in iPSC differentiation into DARPP-32-positive neurons in vitro and in vivo. Further, correction of the HD-iPSCs normalized pathogenic HD signaling pathways (cadherin, TGF-β, BDNF, and caspase activation) and reversed disease phenotypes such as susceptibility to cell death and altered mitochondrial bioenergetics in neural stem cells. The ability to make patient-specific, genetically corrected iPSCs from HD patients will provide relevant disease models in identical genetic backgrounds and is a critical step for the eventual use of these cells in cell replacement therapy.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bachoud-Lévi AC, Gaura V, Brugières P, Lefaucheur JP, Boissé MF, Maison P, Baudic S, Ribeiro MJ, Bourdet C, Remy P, et al. Effect of fetal neural transplants in patients with Huntington’s disease 6 years after surgery: a long-term follow-up study. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Costa M, Dottori M, Sourris K, Jamshidi P, Hatzistavrou T, Davis R, Azzola L, Jackson S, Lim SM, Pera M, et al. A method for genetic modification of human embryonic stem cells using electroporation. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:792–796. - PubMed
-
- Davis RP, Grandela C, Sourris K, Hatzistavrou T, Dottori M, Elefanty AG, Stanley EG, Costa M. Generation of human embryonic stem cell reporter knock-in lines by homologous recombination. Curr. Protoc. Stem Cell Biol. 2009 Chapter 5, Unit 5B 1 1 1-34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

