Associations of urinary levels of kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) with kidney function decline in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
- PMID: 22749388
- PMCID: PMC3690926
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.05.014
Associations of urinary levels of kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) with kidney function decline in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
Abstract
Background: Whether elevations in levels of urinary biomarkers of tubular injury (urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin [NGAL] and kidney injury molecule 1 [KIM-1]) are associated with future risk of kidney disease has not been investigated.
Study design: 1:1 nested case-control study.
Setting & participants: 686 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).
Predictor: NGAL and KIM-1 were measured at baseline, expressed as log-transformed continuous variables, and categorized into deciles.
Outcomes: Kidney function was estimated by cystatin C level using the CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) equation. Incident CKD stage 3 was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m(2) and an eGFR decrease >1 mL/min/1.73 m(2) per year, and rapid kidney function decrease was defined as decrease ≥3 mL/min/1.73 m(2) per year.
Measurements: Cases were defined as persons with eGFR >60 mL/min/1.73 m(2) who subsequently developed incident CKD stage 3 and/or had rapid kidney function decrease by the MESA year-5 visit. Controls were matched for age, sex, race, diabetes, and baseline eGFR. We adjusted for age, hypertension, and presence of albuminuria (albumin-creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g).
Results: Of 343 cases, 145 had incident CKD stage 3, 141 had rapid kidney function decrease, and 57 had both. Mean eGFR for controls was 81 ± 10 mL/min/1.73 m(2) at baseline and 80 ± 10 mL/min/1.73 m(2) at follow-up compared with 82 ± 13 and 58 ± 10 mL/min/1.73 m(2) for cases. Each doubling of KIM-1 level (in picograms per milliliter) was associated with an OR of 1.15 (95% CI, 1.02-1.29) for incident CKD stage 3 and/or rapid kidney function decrease. Compared with the lowest 90%, the highest decile of KIM-1 level was associated with an OR of 2.02 (95% CI, 1.15-3.56) for the outcome; these associations were independent of albuminuria. NGAL levels (in nanograms per milliliter) were not associated with incident CKD stage 3 and/or rapid kidney function decrease (OR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.99-1.10). Results were similar when KIM-1 and NGAL levels were standardized for urine creatinine.
Limitations: The case-control design limits the ability to account for persons who died or were not available for follow-up.
Conclusions: Urinary KIM-1 level is associated with future risk of kidney disease independent of albuminuria. Urinary biomarkers of tubular injury are a promising tool for identifying persons at risk of CKD.
Copyright © 2012 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
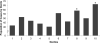
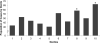
References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Jama. 2007;298:2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Culleton B, Wilson PW, Levy D. Predictors of new-onset kidney disease in a community-based population. JAMA. 2004;291:844–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK082793/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23DK082793-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027002/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

