Siglec-8 as a drugable target to treat eosinophil and mast cell-associated conditions
- PMID: 22749793
- PMCID: PMC3587973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.06.005
Siglec-8 as a drugable target to treat eosinophil and mast cell-associated conditions
Abstract
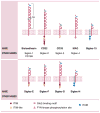
Siglecs (sialic acid immunoglobulin-like lectins) are members of the immunoglobulin gene family that contain sialoside binding N-terminal domains. They are cell surface proteins found predominantly on cells of the immune system. Among them, Siglec-8 is uniquely expressed by human eosinophils and mast cells, as well as basophils. Engaging this structure with antibodies or glycan ligands results in apoptosis in human eosinophils and inhibition of release of preformed and newly generated mediators from human mast cells without affecting their survival. Pro-apoptotic effects are also seen when its closest functional paralog, Siglec-F, on mouse eosinophils is similarly engaged in vitro, and beneficial effects are observed after administration of Siglec-F antibody using models of eosinophilic pulmonary and gastrointestinal inflammation in vivo. Siglec-8 targeting may thus provide a means to specifically inhibit or deplete these cell types. Cell-directed therapies are increasingly sought after by the pharmaceutical industry for their potential to reduce side effects and increase safety. The challenge is to identify suitable targets on the cell type of interest, and selectively deliver a therapeutic agent. By targeting Siglec-8, monoclonal antibodies and glycan ligand-conjugated nanoparticles may be ideally suited for treatment of eosinophil and mast cell-related diseases, such as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, chronic urticaria, hypereosinophilic syndromes, mast cell and eosinophil malignancies and eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest statement
Dr. Bochner is a co-inventor on existing and pending Siglec-8-related patents. Dr. Bochner may be entitled to a share of royalties received by the University on the potential sales of such products. Dr. Bochner is also a co-founder of, and owns stock in, Allakos, Inc., which makes him subject to certain restrictions under University policy. The terms of this arrangement are being managed by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. Drs. Paulson and Kawasaki are inventors on patent applications managed by The Scripps Research Institute relating to the use of siglec ligands for targeting siglec-bearing cells, and they may be entitled to a share of license revenues in the event that they are realized.
Figures


References
-
- Aizawa H, Plitt J, Bochner BS. Human eosinophils express two siglec-8 splice variants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:176. - PubMed
-
- Aizawa H, Zimmermann N, Carrigan PE, Lee JJ, Rothenberg ME, Bochner BS. Molecular analysis of human Siglec-8 orthologs relevant to mouse eosinophils: identification of mouse orthologs of Siglec-5 (mSiglec-F) and Siglec-10 (mSiglec-G) Genomics. 2003;82:521–530. - PubMed
-
- Angata T, Hingorani R, Varki NM, Varki A. Cloning and characterization of a novel mouse Siglec, mSiglec-F: differential evolution of the mouse and human (CD33) Siglec-3-related gene clusters. J Biol Chem. 2001a;276:45128–45136. - PubMed
-
- Angata T, Varki NM, Varki A. A second uniquely human mutation affecting sialic acid biology. J Biol Chem. 2001b;276:40282–40287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

