Stimulation of adenosine receptors in the nucleus accumbens reverses the expression of cocaine sensitization and cross-sensitization to dopamine D2 receptors in rats
- PMID: 22749927
- PMCID: PMC3427408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.038
Stimulation of adenosine receptors in the nucleus accumbens reverses the expression of cocaine sensitization and cross-sensitization to dopamine D2 receptors in rats
Abstract
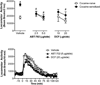
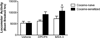
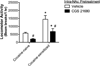
Adenosine receptors co-localize with dopamine receptors on medium spiny nucleus accumbens (NAc) neurons where they antagonize dopamine receptor activity. It remains unclear whether adenosine receptor stimulation in the NAc restores cocaine-induced enhancements in dopamine receptor sensitivity. The goal of these studies was to determine whether stimulating A(1) or A(2A) receptors in the NAc reduces the expression of cocaine sensitization. Rats were sensitized with 7 daily treatments of cocaine (15 mg/kg, i.p.). Following one-week withdrawal, the effects of intra-NAc microinjections of the adenosine kinase inhibitor (ABT-702), the adenosine deaminase inhibitor (deoxycoformycin; DCF), the specific A(1) receptor agonist (CPA) and the specific A(2A) receptor agonist (CGS 21680) were tested on the behavioral expression of cocaine sensitization. The results indicate that intra-NAc pretreatment of ABT-702 and DCF dose-dependently blocked the expression of cocaine sensitization while having no effects on acute cocaine sensitivity, suggesting that upregulation of endogenous adenosine in the accumbens is sufficient to non-selectively stimulate adenosine receptors and reverse the expression of cocaine sensitization. Intra-NAc treatment of CPA significantly inhibited the expression of cocaine sensitization, which was reversed by both A(1) and A(2A) receptor antagonism. Intra-NAc treatment of CGS 21680 also significantly inhibited the expression of cocaine sensitization, which was selectively reversed by A(2A), but not A(1), receptor antagonism. Finally, CGS 21680 also inhibited the expression of quinpirole cross-sensitization. Together, these findings suggest that adenosine receptor stimulation in the NAc is sufficient to reverse the behavioral expression of cocaine sensitization and that A(2A) receptors blunt cocaine-induced sensitization of postsynaptic D(2) receptors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


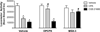
Similar articles
-
Persistent reduction of cocaine seeking by pharmacological manipulation of adenosine A1 and A 2A receptors during extinction training in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Aug;231(16):3179-88. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3489-2. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24562064 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2A receptors in the nucleus accumbens bi-directionally alter cocaine seeking in rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Apr;37(5):1245-56. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.312. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22169945 Free PMC article.
-
The adenosine A(2A) receptor agonist CGS 21680 alleviates auditory sensorimotor gating deficits and increases in accumbal CREB in rats neonatally treated with quinpirole.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Dec;237(12):3519-3527. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05631-8. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32772144 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-medial prefrontal cortex injection of quinpirole, but not SKF 38393, blocks the acute motor-stimulant response to cocaine in the rat.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000 Aug;151(2-3):211-8. doi: 10.1007/s002139900345. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000. PMID: 10972467
-
Dopamine/adenosine interactions involved in effort-related aspects of food motivation.Appetite. 2009 Dec;53(3):422-5. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2009.07.018. Epub 2009 Jul 25. Appetite. 2009. PMID: 19635514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent reduction of cocaine seeking by pharmacological manipulation of adenosine A1 and A 2A receptors during extinction training in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Aug;231(16):3179-88. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3489-2. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24562064 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dopamine D2-like receptors and their modulation by adenosine receptor stimulation in the reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Apr;236(4):1207-1218. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5126-y. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30470862 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic diet, adenosine, and dopamine in addiction and psychiatry.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 10;12:1492306. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1492306. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40129664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeine, a common active adulterant of cocaine, enhances the reinforcing effect of cocaine and its motivational value.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Aug;233(15-16):2879-89. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4320-z. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27270948
-
Reduced sleep duration mediates decreases in striatal D2/D3 receptor availability in cocaine abusers.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Mar 8;6(3):e752. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.14. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26954979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JU, Careri JM, Efferen TR, Rotrosen J. Differential effects of dopamine antagonists on locomotor activity, conditioned activity and conditioned place preference induced by cocaine in rats. Behav Pharmacol. 2001;12:603–611. - PubMed
-
- Alexander SP, Reddington M. The cellular localization of adenosine receptors in rat neostriatum. Neuroscience. 1989;28:645–651. - PubMed
-
- Arch JR, Newsholme EA. Activities and some properties of 5'-nucleotidase, adenosine kinase and adenosine deaminase in tissues from vertebrates and invertebrates in relation to the control of the concentration and the physiological role of adenosine. The Biochemical journal. 1978;174:965–977. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Ghorayeb I, Normand E, Bloch B. Phenotypical characterization of the neurons expressing the D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the monkey striatum. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 2000;418:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Bachtell RK, Whisler K, Karanian D, Self DW. Effects of intra-nucleus accumbens shell administration of dopamine agonists and antagonists on cocaine-taking and cocaine-seeking behaviors in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;183:41–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

