Structure of the signal transduction protein TRAP (target of RNAIII-activating protein)
- PMID: 22750855
- PMCID: PMC3388912
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309112020167
Structure of the signal transduction protein TRAP (target of RNAIII-activating protein)
Abstract
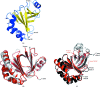
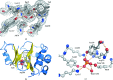
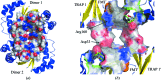
The crystal structure of the signal transduction protein TRAP is reported at 1.85 Å resolution. The structure of TRAP consists of a central eight-stranded β-barrel flanked asymmetrically by helices and is monomeric both in solution and in the crystal structure. A formate ion was found bound to TRAP identically in all four molecules in the asymmetric unit.
Figures
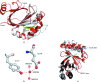
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221.
-
- Arnold, K., Bordoli, L., Kopp, J. & Schwede, T. (2006). Bioinformatics, 22, 195–201. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N., Goldkorn, T., Gov, Y., Hirshberg, M., Koyfman, N., Matthews, H. R., Nhan, R. T., Singh, B. & Uziel, O. (2001). J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2658–2667. - PubMed
-
- Dauter, Z., Dauter, M. & Rajashankar, K. R. (2000). Acta Cryst. D56, 232–237. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

