p16(INK4A) represses the paracrine tumor-promoting effects of breast stromal fibroblasts
- PMID: 22751126
- PMCID: PMC3679618
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.270
p16(INK4A) represses the paracrine tumor-promoting effects of breast stromal fibroblasts
Erratum in
- Oncogene. 2013 May 2;32(18):2372
Abstract
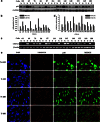
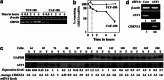
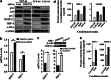
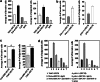
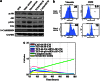
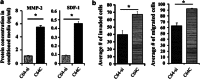
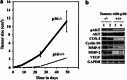
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), the most abundant and probably the most active cellular component of breast cancer-associated stroma, promote carcinogenesis through paracrine effects; however, the molecular basis remains elusive. We have shown here that p16(INK4A) expression is reduced in 83% CAFs as compared with their normal adjacent counterparts cancer-free tissues isolated from the same patients. This decrease is mainly due to AUF1-dependent higher turnover of the CDKN2A mRNA in CAFs. Importantly, p16(INK4A) downregulation using specific siRNA activated breast fibroblasts and increased the expression/secretion levels of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2. Consequently, media conditioned with these cells stimulated the proliferation of epithelial cells. Furthermore, the migration/invasion of breast cancer cells was also enhanced in an SDF-1-dependent manner. This effect was mediated through inducing an epithelial-mesenchymal transition state. By contrast, increase in p16(INK4A) level through ectopic expression or AUF1 downregulation, reduced the secreted levels of SDF-1 and MMP-2 and suppressed the pro-carcinogenic effects of CAFs. In addition, p16(INK4A)-defective fibroblasts accelerated breast tumor xenograft formation and growth rate in mice. Importantly, tumors formed in the presence of p16(INK4A)-defective fibroblasts exhibited higher levels of active Akt, Cox-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9, showing their greater aggressiveness as compared with xenografts formed in the presence of p16(INK4A)-proficient fibroblasts. These results provide the first indication that p16(INK4A) downregulation in breast stromal fibroblasts is an important step toward their activation.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. Ca Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Dong-Le Bourhis X, Berthois Y, Millot G, Degeorges A, Sylvi M, Martin PM, et al. Effect of stromal and epithelial cells derived from normal and tumorous breast tissue on the proliferation of human breast cancer cell lines in co-culture. Int J Cancer. 1997;71:42–48. - PubMed
-
- Kim JB, Stein R, O'Hare MJ. Tumour-stromal interactions in breast cancer: the role of stroma in tumourigenesis. Tumour Biol. 2005;26:173–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

