Development and homeostasis of the skin epidermis
- PMID: 22751151
- PMCID: PMC3385954
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008383
Development and homeostasis of the skin epidermis
Abstract
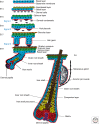
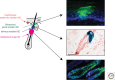
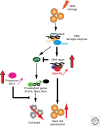
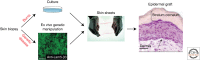
The skin epidermis is a stratified epithelium that forms a barrier that protects animals from dehydration, mechanical stress, and infections. The epidermis encompasses different appendages, such as the hair follicle (HF), the sebaceous gland (SG), the sweat gland, and the touch dome, that are essential for thermoregulation, sensing the environment, and influencing social behavior. The epidermis undergoes a constant turnover and distinct stem cells (SCs) are responsible for the homeostasis of the different epidermal compartments. Deregulation of the signaling pathways controlling the balance between renewal and differentiation often leads to cancer formation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Building epithelial tissues from skin stem cells.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:333-50. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.032. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008. PMID: 19022769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Label retaining cells (LRCs) with myoepithelial characteristic from the proximal acinar region define stem cells in the sweat gland.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 18;8(9):e74174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074174. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24058524 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct epidermal stem cell compartments are maintained by independent niche microenvironments.Stem Cell Rev. 2006;2(3):221-31. doi: 10.1007/s12015-006-0050-7. Stem Cell Rev. 2006. PMID: 17625258 Review.
-
Heterogeneity and plasticity of epidermal stem cells.Development. 2014 Jul;141(13):2559-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.104588. Development. 2014. PMID: 24961797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms regulating epidermal stem cells.EMBO J. 2012 May 2;31(9):2067-75. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.67. Epub 2012 Mar 20. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22433839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial Label-Retaining Cells Are Absent during Tooth Cycling in Salmo salar and Polypterus senegalus.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 6;11(4):e0152870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152870. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27049953 Free PMC article.
-
Abalone Collagen Extracts Potentiate Stem Cell Properties of Human Epidermal Keratinocytes.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jul 20;17(7):424. doi: 10.3390/md17070424. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31330853 Free PMC article.
-
Differential antigen expression between human eccrine sweat glands and hair follicles/pilosebaceous units.J Mol Histol. 2019 Aug;50(4):335-342. doi: 10.1007/s10735-019-09830-2. Epub 2019 May 6. J Mol Histol. 2019. PMID: 31062203
-
Learning from regeneration research organisms: The circuitous road to scar free wound healing.Dev Biol. 2018 Jan 15;433(2):144-154. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.09.025. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29179946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics in Skin Homeostasis and Ageing.Epigenomes. 2025 Jan 9;9(1):3. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes9010003. Epigenomes. 2025. PMID: 39846570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adolphe C, Hetherington R, Ellis T, Wainwright B 2006. Patched1 functions as a gatekeeper by promoting cell cycle progression. Cancer Res 66: 2081–2088 - PubMed
-
- Alam M, Ratner D 2001. Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 344: 975–983 - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Reddy ST, Gaddapara T, Millar SE 2002. WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev Cell 2: 643–653 - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Ahn K, Kairo A, Chu EY, Wine-Lee L, Reddy ST, Croft NJ, Cebra-Thomas JA, Metzger D, Chambon P, et al. 2004. Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development 131: 2257–2268 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
