Increase in recombination rate in Arabidopsis thaliana plants sharing gaseous environment with X-ray and UVC-irradiated plants depends on production of radicals
- PMID: 22751301
- PMCID: PMC3583963
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.20571
Increase in recombination rate in Arabidopsis thaliana plants sharing gaseous environment with X-ray and UVC-irradiated plants depends on production of radicals
Abstract
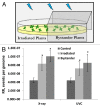
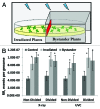
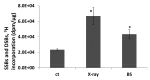
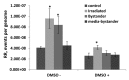
X-ray and UVC are the two physical agents that damage DNA directly, with both agents capable of inducing double-strand breaks. Some of our recent work has demonstrated that local exposure to UVC results in a systemic increase in recombination frequency, suggesting that information about exposure can be passed from damaged to non-damaged tissue. Indeed, we recently showed that plants sharing the same enclosed environment with UVC-irradiated plants exhibit similar increase in homologous recombination frequency as irradiated plants. Here, we further tested whether yet another DNA-damaging agent, X-ray, is capable of increasing recombination rate (RR) in neighboring plants grown in a Petri dish. To test this, we grew plants exposed to X-ray or UVC irradiation in an enclosed environment next to non-exposed plants. We found that both X-ray and UVC-irradiated plants and neighboring plants exhibited comparable increases in the levels of strand breaks and the RR. We further showed that pre-exposure of plants to radical scavenger DMSO substantially alleviates the radiation-induced increase in RR and prevents formation of bystander signal. Our results suggest that the increase in RR in bystander plants can also be triggered by X-ray and that radicals may play some role in initiation or maintenance of this signal.
Figures
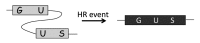

Similar articles
-
Genome stability of Arabidopsis atm, ku80 and rad51b mutants: somatic and transgenerational responses to stress.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Jun;54(6):982-9. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct051. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23574700
-
Perception of volatiles produced by UVC-irradiated plants alters the response to viral infection in naïve neighboring plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Jul;7(7):741-5. doi: 10.4161/psb.20406. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22751319 Free PMC article.
-
UV-C-irradiated Arabidopsis and tobacco emit volatiles that trigger genomic instability in neighboring plants.Plant Cell. 2011 Oct;23(10):3842-52. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.089003. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 22028460 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of DNA damage and repair: progress in plants.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;36(4):337-97. doi: 10.1080/20014091074219. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11563486 Review.
-
[The main repair pathways of double-strand breaks in the genomic DNA and interactions between them].Tsitol Genet. 2014 May-Jun;48(3):64-77. Tsitol Genet. 2014. PMID: 25019146 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Stress Management in Plants: Examining Provisional and Unique Dose-Dependent Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5105. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065105. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shulaev V, Silverman P, Raskin I. Airborne signalling by methyl salicylate in plant pathogen resistance. Nature. 1997;385:718–21. doi: 10.1038/385718a0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
