Attenuation of cytokinin signaling via proteolysis of a type-B response regulator
- PMID: 22751310
- PMCID: PMC3583957
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.20469
Attenuation of cytokinin signaling via proteolysis of a type-B response regulator
Abstract
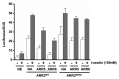
Type-B response regulators (ARRs) are a group of transcription factors that are activated by cytokinin-initiated phospho-relays and regulate the expression of cytokinin-responsive genes. Recently, we reported that proteolysis of ARR2 in Arabidopsis is facilitated by cytokinins, resulting in attenuation of the signaling output of two-component circuitry. Interestingly, despite similarities in the primary structures and conserved receiver domains, the proteolytic properties of ARR2 are distinct from those of the other type-B ARRs. Using a gain-of-function mutant (ARR2(K90G)) resistant to protein degradation, we clearly demonstrated that increased levels of ARR2 affected cytokinin-mediated processes such as primary root growth, callus induction, hypocotyl elongation and leaf senescence. At the molecular level, expression of type-A ARRs was increased in transgenics expressing ARR2(K90G), resulting in enhanced cytokinin sensitivity. Here, we describe these findings and how they may be incorporated into the currently accepted model for the regulation of cytokinin signaling. In addition, we describe the proteomic approaches used to identify proteins that interact with ARR2. The putative roles of ARR2 proteolysis are also addressed with regard to other developmental processes. In conclusion, cytokinin-facilitated degradation of ARR2 must be appreciated as a post-translational event important for regulating cytokinin signaling intensity.
Figures
References
-
- Choi J, Hwang I. Cytokinin: perception, signal transduction, and role in plant growth and development. J Plant Biol. 2007;50:98–108. doi: 10.1007/BF03030617. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
